- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录261240 > IBM25PPC750GXEBB1033T 32-BIT, 733 MHz, RISC PROCESSOR, CBGA292 PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | IBM25PPC750GXEBB1033T |
| 元件分类: | 微控制器/微处理器 |
| 英文描述: | 32-BIT, 733 MHz, RISC PROCESSOR, CBGA292 |
| 封装: | 21 X 21 MM, 1 MM PITCH, CERAMIC, BGA-292 |
| 文件页数: | 59/74页 |
| 文件大小: | 1054K |
| 代理商: | IBM25PPC750GXEBB1033T |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页当前第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页
Datasheet
IBM PowerPC 750GX RISC Microprocessor
DD1.X
System Design Information
Page 62 of 73
750GX_ds_body.fm SA14-2765-02
September 2, 2005
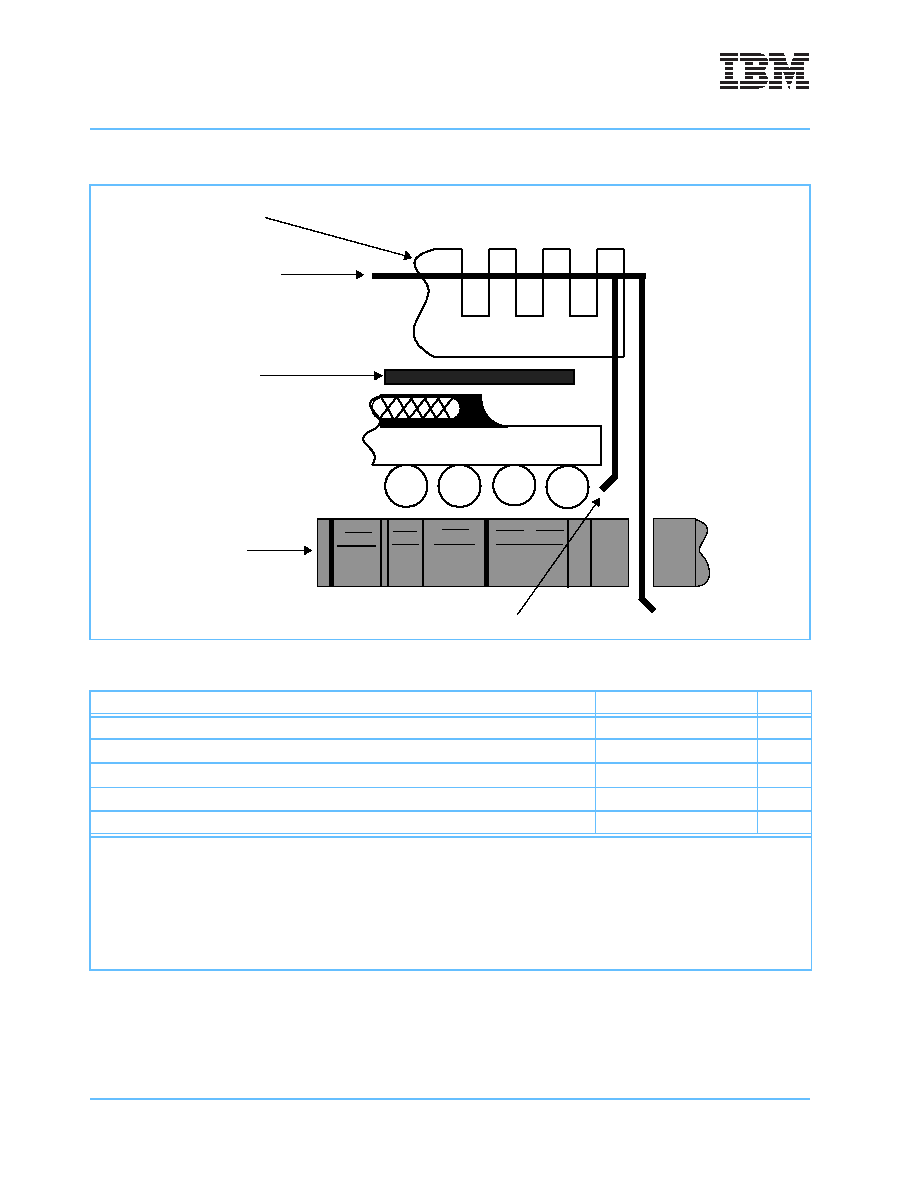
The board designer can choose between several types of heat sinks to place on the 750GX. There are
several commercially-available heat sinks for the 750GX provided by the vendors listed in Table 5-8, 750GX
Figure 5-7. Package Exploded Cross-Sectional View with Several Heat-Sink Options
Table 5-7. Maximum Heat-Sink Weight Limit for the CBGA
Force
Maximum
Notes
Maximum dynamic compressive force allowed on the BGA balls
42.9 N
Maximum dynamic tensile force allowed on the BGA balls
9.05 N
Maximum dynamic compressive force allowed on the chip
22.4 N
Maximum mass of module + heat sink when heat sink is not bolted to card
39 g
Maximum torque on die (or substrate)
28in-lbs
1. The maximum instantaneous compressive force distributed across the module surface, and perpendicular to the surface of the
board on which it is mounted.
2. The maximum instantaneous tensile force exerted across the module surface, and perpendicular to the surface of the board on
which it is mounted.
3. The maximum instantaneous compressive force distributed across the die surface, and perpendicular to the surface of the board
on which it is mounted.
4. The maximum combined mass of the module, attached heat sink or spreader, and adhesive material used to secure or support the
heat sink or spreader to the module’s ceramic surface.
CBGA Package
Heat Sink
Heat Sink Clip
Adhesive
Printed
Option
Circuit
Board
or
Thermal
Interface
Material
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ICS525-01RILF | 140 MHz, OTHER CLOCK GENERATOR, PDSO28 |
| ICS954119YF-T | 400 MHz, PROC SPECIFIC CLOCK GENERATOR, PDSO56 |
| ICS181M-01T | 75 MHz, OTHER CLOCK GENERATOR, PDSO8 |
| IT80C32E-30R | 8-BIT, 30 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
| IT80C154-16R | 8-BIT, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| IBM25PPC750GXEBB2562T | 制造商:IBM 功能描述: |
| IBM25PPC750GXEBB2563T | 制造商:IBM 功能描述: |
| IBM25PPC750GXECB2563T | 制造商:IBM 功能描述: |
| IBM25PPC750GXECB2H33T | 制造商:IBM 功能描述: |
| IBM25PPC750GXECB5H42V | 制造商:IBM 功能描述:POLARIS 1.2 ? 21CBGA GRE2 ? HALFMODE 933MH - Trays |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。