参数资料
| 型号: | ISL6334IRZ |
| 厂商: | Intersil |
| 文件页数: | 27/31页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC CTRLR PWM 4PHASE BUCK 40-QFN |
| 标准包装: | 50 |
| 应用: | 控制器,Intel VR11.1 |
| 输入电压: | 3 V ~ 12 V |
| 输出数: | 1 |
| 输出电压: | 0.5 V ~ 1.6 V |
| 工作温度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 安装类型: | 表面贴装 |
| 封装/外壳: | 40-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 |
| 供应商设备封装: | 40-QFN(6x6) |
| 包装: | 管件 |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页当前第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页
�� �
�
 �
�ISL6334,� ISL6334A�
�where� I� FL� is� the� full� load� current� of� the� specific� application,�
�and� VR� DROOP� is� the� desired� voltage� droop� under� the� full�
�load� condition.�
�C� 2� (OPTIONAL)�
�Based� on� the� desired� loadline� R� LL� ,� the� loadline� regulation�
�R� C�
�C� C�
�COMP�
�resistor� can� be� calculated� using� Equation� 33:�
�NR� R�
�R� FB� =� ----------------------------------�
�ISEN� LL�
�R� X�
�(EQ.� 33)�
�FB�
�where� N� is� the� active� channel� number,� R� ISEN� is� the� sense�
�resistor� connected� to� the� ISEN+� pin,� and� R� X� is� the�
�resistance� of� the� current� sense� element,� either� the� DCR� of�
�R� FB�
�+�
�V� DROOP�
�-�
�VDIFF�
�the� inductor� or� R� SENSE� depending� on� the� sensing� method.�
�∑� R� ISEN� (� n� )�
�R� X�
�If� one� or� more� of� the� current� sense� resistors� are� adjusted� for�
�thermal� balance� (as� in� Equation� 31),� the� load-line� regulation�
�resistor� should� be� selected� based� on� the� average� value� of�
�the� current� sensing� resistors,� as� given� in� Equation� 34:�
�R� LL�
�R� FB� =� ----------� (EQ.� 34)�
�n�
�where� R� ISEN(n)� is� the� current� sensing� resistor� connected� to�
�the� n� th� ISEN+� pin.�
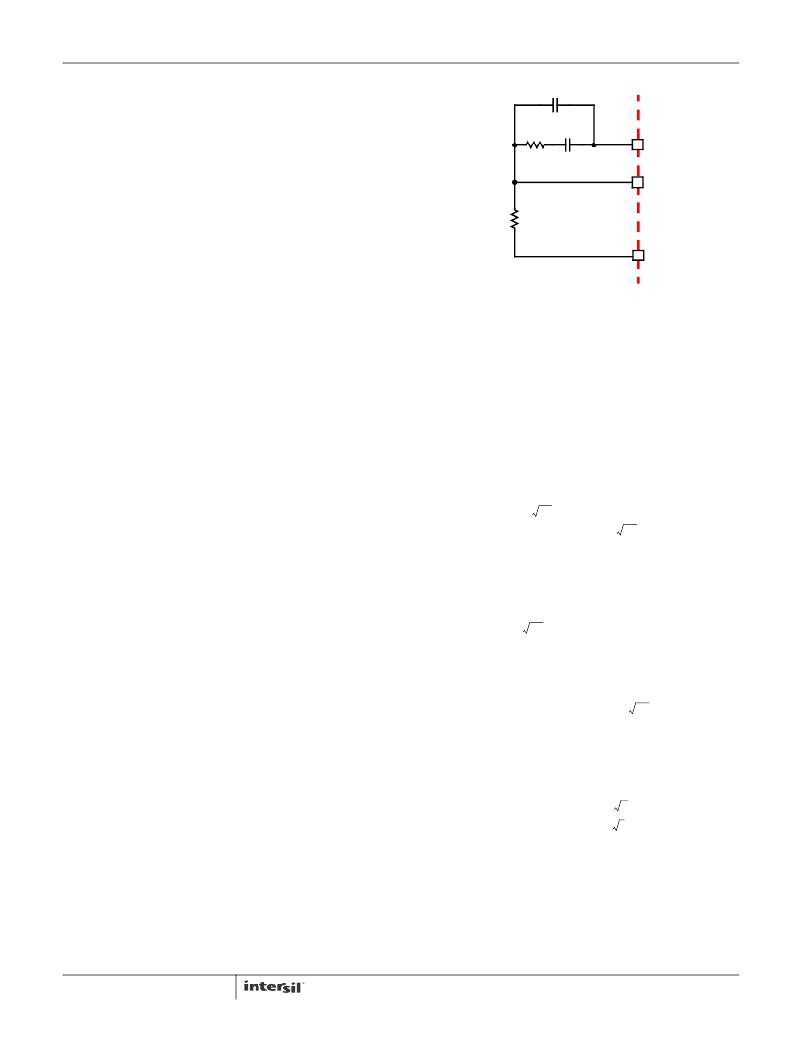
�Compensation�
�The� two� opposing� goals� of� compensating� the� voltage�
�regulator� are� stability� and� speed.� Depending� on� whether� the�
�regulator� employs� the� optional� load-line� regulation� as�
�FIGURE� 17.� COMPENSATION� CONFIGURATION� FOR�
�LOAD-LINE� REGULATED� ISL6334,� ISL6334A�
�CIRCUIT�
�The� feedback� resistor,� R� FB� ,� has� already� been� chosen� as�
�outlined� in� “Load-Line� Regulation� Resistor”� on� page� 26.�
�Select� a� target� bandwidth� for� the� compensated� system,� f� 0� .�
�The� target� bandwidth� must� be� large� enough� to� assure�
�adequate� transient� performance,� but� smaller� than� 1/3� of� the�
�per-channel� switching� frequency.� The� values� of� the�
�compensation� components� depend� on� the� relationships� of� f� 0�
�to� the� L-C� pole� frequency� and� the� ESR� zero� frequency.� For�
�each� of� the� three� cases� which� follow,� there� is� a� separate� set�
�of� equations� for� the� compensation� components.�
�-------------------� >� f� 0�
�R� C� =� R� FB� --------------------------------------�
�0.75V�
�2� π� V� P-P� R� FB� f� 0�
�-------------------� ≤� f� 0� <� ------------------------------�
�described� in� Load-Line� Regulation,� there� are� two� distinct�
�methods� for� achieving� these� goals.�
�COMPENSATING� LOAD-LINE� REGULATED�
�CONVERTER�
�The� load-line� regulated� converter� behaves� in� a� similar�
�manner� to� a� peak-current� mode� controller� because� the� two�
�poles� at� the� output-filter� L-C� resonant� frequency� split� with�
�the� introduction� of� current� information� into� the� control� loop.�
�The� final� location� of� these� poles� is� determined� by� the� system�
�Case� 1:�
�Case� 2:�
�1�
�2� π� LC�
�2� π� f� 0� V� P-P� LC�
�IN�
�0.75V� IN�
�C� C� =� -------------------------------------�
�1� 1�
�2� π� LC� 2� π� C� (� ESR� )�
�0.75� V� IN�
�(� 2� π� )� 2� f� 02� V� P-P� R� FB� LC�
�function,� the� gain� of� the� current� signal,� and� the� value� of� the�
�compensation� components,� R� C� and� C� C� .�
�Since� the� system� poles� and� zero� are� affected� by� the� values�
�of� the� components� that� are� meant� to� compensate� them,� the�
�solution� to� the� system� equation� becomes� fairly� complicated.�
�V� P-P� (� 2� π� )� 2� f� 02� LC�
�R� C� =� R� FB� ----------------------------------------------�
�0.75V� IN�
�C� C� =� --------------------------------------------------------------�
�(EQ.� 35)�
�f� 0� >� ------------------------------�
�0.75� V� IN� (� ESR� )�
�2� π� V� P-P� R� FB� f� 0� L�
�Fortunately� there� is� a� simple� approximation� that� comes� very�
�close� to� an� optimal� solution.� Treating� the� system� as� though� it�
�were� a� voltage-mode� regulator� by� compensating� the� L-C�
�poles� and� the� ESR� zero� of� the� voltage-mode� approximation�
�yields� a� solution� that� is� always� stable� with� very� close� to� ideal�
�transient� performance.�
�Case� 3:�
�1�
�2� π� C� (� ESR� )�
�2� π� f� 0� V� P-P� L�
�R� C� =� R� FB� ------------------------------------------�
�0.75V� IN� (� ESR� )� C�
�C� C� =� -------------------------------------------------�
�In� Equation� 35,� L� is� the� per-channel� filter� inductance� divided�
�by� the� number� of� active� channels;� C� is� the� sum� total� of� all�
�output� capacitors;� ESR� is� the� equivalent-series� resistance� of�
�the� bulk� output-filter� capacitance;� and� V� PP� is� the� sawtooth�
�amplitude� described� in� the� “Electrical� Specifications”� table�
��27�
�FN6482.2�
�February� 1,� 2013�
�相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| X40015S8I-A | IC VOLTAGE MONITOR DUAL 8-SOIC |
| X40015S8-CT1 | IC VOLTAGE MONITOR DUAL 8-SOIC |
| RMC26DRTN-S13 | CONN EDGECARD 52POS .100 EXTEND |
| X40015V8I-AT1 | IC VOLTAGE MONITOR DUAL 8-TSSOP |
| EMA30DRSD-S273 | CONN EDGECARD 60POS DIP .125 SLD |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| ISL6334IRZ-T | 功能描述:IC CTRLR PWM 4PHASE BUCK 40-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 稳压器 - 专用型 系列:- 标准包装:43 系列:- 应用:控制器,Intel VR11 输入电压:5 V ~ 12 V 输出数:1 输出电压:0.5 V ~ 1.6 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:48-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:48-QFN(7x7) 包装:管件 |
| ISL6336ACRZ | 功能描述:IC CTRLR PWM 6PHASE BUCK 48-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 稳压器 - 专用型 系列:- 标准包装:43 系列:- 应用:控制器,Intel VR11 输入电压:5 V ~ 12 V 输出数:1 输出电压:0.5 V ~ 1.6 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:48-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:48-QFN(7x7) 包装:管件 |
| ISL6336ACRZ-T | 功能描述:IC CTRLR PWM 6PHASE BUCK 48-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 稳压器 - 专用型 系列:- 标准包装:43 系列:- 应用:控制器,Intel VR11 输入电压:5 V ~ 12 V 输出数:1 输出电压:0.5 V ~ 1.6 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:48-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:48-QFN(7x7) 包装:管件 |
| ISL6336AIRZ | 功能描述:IC CTRLR PWM 6PHASE BUCK 48-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 稳压器 - 专用型 系列:- 标准包装:43 系列:- 应用:控制器,Intel VR11 输入电压:5 V ~ 12 V 输出数:1 输出电压:0.5 V ~ 1.6 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:48-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:48-QFN(7x7) 包装:管件 |
| ISL6336AIRZ-T | 功能描述:IC CTRLR PWM 6PHASE BUCK 48-QFN RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> PMIC - 稳压器 - 专用型 系列:- 标准包装:43 系列:- 应用:控制器,Intel VR11 输入电压:5 V ~ 12 V 输出数:1 输出电压:0.5 V ~ 1.6 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:48-VFQFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:48-QFN(7x7) 包装:管件 |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。