- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录378041 > PBL388131SOT (ERICSSON) Voice-switched Speakerphone Circuit with built in loudspeaker amplifier PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | PBL388131SOT |
| 厂商: | ERICSSON |
| 英文描述: | Voice-switched Speakerphone Circuit with built in loudspeaker amplifier |
| 中文描述: | 语音交换与内置免提扬声器放大器电路 |
| 文件页数: | 12/16页 |
| 文件大小: | 299K |
| 代理商: | PBL388131SOT |
12
PBL 388 13
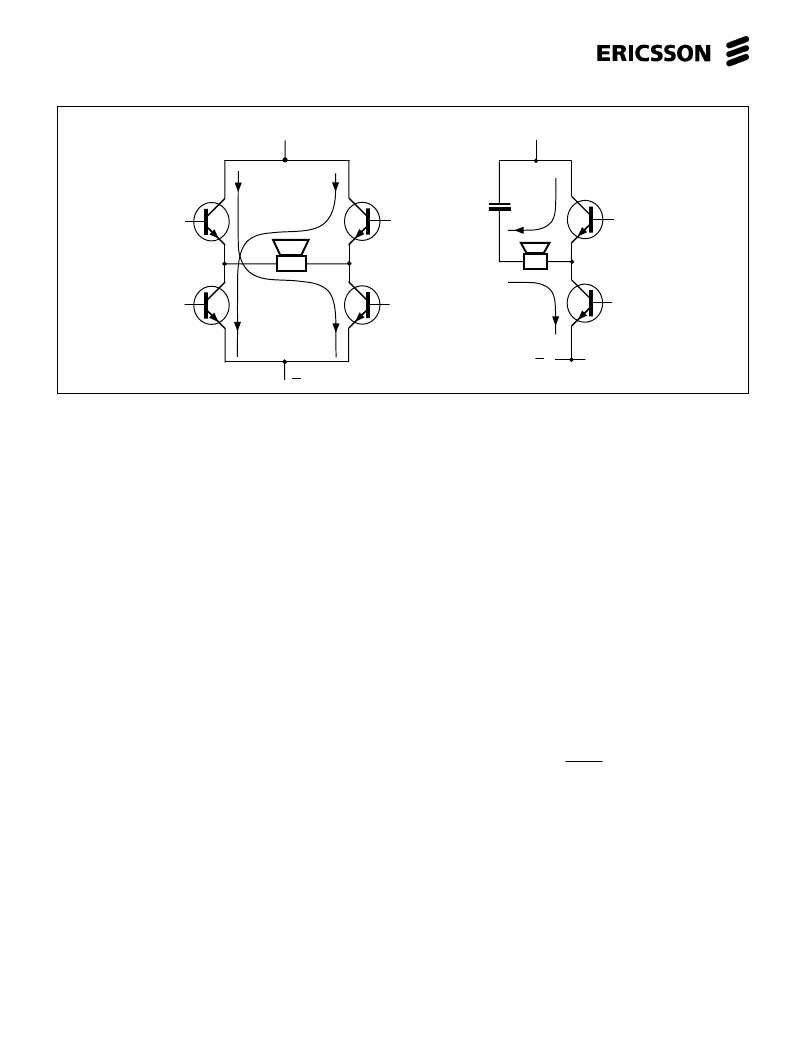
Figure 26. Power amplifier systems.
push - pull
+
+
+
single ended
I
I
I
I
here that such a line will give 45mA. As
calculated above the speech and handsfree
circuits use 10mA so 35mA can be used to
drive the speaker. The power will be I2 x R
= 0.035 x 0.035 x 50 = 61.25mW. The
supply voltage needed across the reservoir
capacitor is 2 x 1.41 x 0.035 x 50 + 0.85 =
5.8V
In this case the DC - mask has to be
adjusted as high as possible in order to
have enough voltage. The question is if this
high output power is desirable or is a
satisfactory function at low current levels
more important. A solution to this high
voltage level in the above example can be
halving the loudspeaker impedance but
this would of course make the low current
function worse.
The rarely observed fact is, that it is the
lack of current that limits the availability of
power from the telephone line, not the
voltage. This means that a single ended A
- B class amplifier with hardly any stand by
current at all is well suited for the task. This
system will render a high efficiency because
all the available current will pass the
loudspeaker ”sort of twice”. A push-pull
system would be less suitable because it
needs double the current in situation like
this where availability of current is the
limiting factor.This could be overcome by
doubling the impedance of the loudspeaker
but again that kind of loudspeaker is hardly
possible to use ( due to price) even if there
were some available.
A power amplifier in a
handsfree telephone that is
supplied from the line.
Comparison between single ended and
push-pull output stage.
The amplifier has to have as high
efficiency as possible to convert the
available line current into audio power. A
modern telephone line will give, depending
of the line length 20 - 80 mA of current.
Standard loudspeaker impedance range,
that will come into question, (size,price and
availability) is 8 - 50
. The output audio
power requirement (electrical) can be 0 -
100 mW. The acoustical output power will
be greatly dependent of the loudspeaker
efficiency. ( 1 - 15%)
Example:
How much audio power can be
obtained using the PBL 385 41 and PBL
388 13 in a minimum specification case of
6V/20mA at the telephone set Next is to
show how much current really is available
to drive the loudspeaker.
The current consumption of the speech
circuit:
1) 3.4mA for band gap reference,
supply pin 4 and quiscent current for
earphone.
2) 2mA for DC1 that goes to speech
switching in the 388 13.
3) 6.6mA for the transmitter, in order
to be able to transmit 2V peak into 300
load (600
//600
). DTMF in mute
condition.
The current consumption of the
handsfree circuit:
1) 2mA for quiscent current in the
power amplifier
2) 2mA for speech switching (taken
into account in speech circuit)
Adding this up leaves only 6mA to
drive the loudspeaker. Luckily this is not the
whole truth because the transmitter will not
need the whole 6.6mA in receiver mode
where the loudspeaker is used, this will
give some 4mA further to the loudspeaker.
From 20mA line current, 10mA can be used
to drive the speaker.
Assume that a 50
speaker is used,
the power will be P= I2 x R
0.01 x 0.01 x 50 = 5mW (not much, but
audible). If a 16
speaker would have been
used the output would be three times less.
The voltage needed for the supply of this is,
U = I X R; 0.01 x 50 = 0.5V This would be
the RMS value of the voltage across the
loudspeaker. The voltage across the
reservoir capacitor would have to be 2 x
1.41 x 0.5 + (
≈
0.85) = 2.3V (0.85V is the
voltage drop across the transistor). The
question here is of electrical not acoustical
power and the signal used in calculations is
a sine wave. In the real working environment
the signal will be speech and peak power
for speech that can be taken out of the
reservoir capacitor is much higher.
To see how much power can be taken
out from a median CO line, it is assumed
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PBL38813 | Voice-switched Speakerphone Circuit with built in loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL388131N | Voice-switched Speakerphone Circuit with built in loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL388131SO | Voice-switched Speakerphone Circuit with built in loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL38814 | Voice - switched 2-channel Circuit with loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL388141N | Voice - switched 2-channel Circuit with loudspeaker amplifier |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| PBL38814 | 制造商:ERICSSON 制造商全称:Ericsson 功能描述:Voice - switched 2-channel Circuit with loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL388141N | 制造商:ERICSSON 制造商全称:Ericsson 功能描述:Voice - switched 2-channel Circuit with loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL388141SO | 制造商:ERICSSON 制造商全称:Ericsson 功能描述:Voice - switched 2-channel Circuit with loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL388141SOT | 制造商:ERICSSON 制造商全称:Ericsson 功能描述:Voice - switched 2-channel Circuit with loudspeaker amplifier |
| PBL3-RP15 | 制造商:Middle Atlantic Products 功能描述: |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。