- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录3851 > PIC24FJ64GA006-I/MR (Microchip Technology)MCU 64KB FLASH 8KB RAM 64-QFN PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | PIC24FJ64GA006-I/MR |
| 厂商: | Microchip Technology |
| 文件页数: | 200/258页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | MCU 64KB FLASH 8KB RAM 64-QFN |
| 特色产品: | PIC24FJ/33FJ MCUs & dsPIC? DSCs |
| 标准包装: | 40 |
| 系列: | PIC® 24F |
| 核心处理器: | PIC |
| 芯体尺寸: | 16-位 |
| 速度: | 16MHz |
| 连通性: | I²C,PMP,SPI,UART/USART |
| 外围设备: | 欠压检测/复位,POR,PWM,WDT |
| 输入/输出数: | 53 |
| 程序存储器容量: | 64KB(22K x 24) |
| 程序存储器类型: | 闪存 |
| RAM 容量: | 8K x 8 |
| 电压 - 电源 (Vcc/Vdd): | 2 V ~ 3.6 V |
| 数据转换器: | A/D 16x10b |
| 振荡器型: | 内部 |
| 工作温度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 封装/外壳: | 64-QFN |
| 包装: | 管件 |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页第90页第91页第92页第93页第94页第95页第96页第97页第98页第99页第100页第101页第102页第103页第104页第105页第106页第107页第108页第109页第110页第111页第112页第113页第114页第115页第116页第117页第118页第119页第120页第121页第122页第123页第124页第125页第126页第127页第128页第129页第130页第131页第132页第133页第134页第135页第136页第137页第138页第139页第140页第141页第142页第143页第144页第145页第146页第147页第148页第149页第150页第151页第152页第153页第154页第155页第156页第157页第158页第159页第160页第161页第162页第163页第164页第165页第166页第167页第168页第169页第170页第171页第172页第173页第174页第175页第176页第177页第178页第179页第180页第181页第182页第183页第184页第185页第186页第187页第188页第189页第190页第191页第192页第193页第194页第195页第196页第197页第198页第199页当前第200页第201页第202页第203页第204页第205页第206页第207页第208页第209页第210页第211页第212页第213页第214页第215页第216页第217页第218页第219页第220页第221页第222页第223页第224页第225页第226页第227页第228页第229页第230页第231页第232页第233页第234页第235页第236页第237页第238页第239页第240页第241页第242页第243页第244页第245页第246页第247页第248页第249页第250页第251页第252页第253页第254页第255页第256页第257页第258页
PIC24FJ128GA010 FAMILY
DS39747F-page 46
2005-2012 Microchip Technology Inc.
4.2.5
SOFTWARE STACK
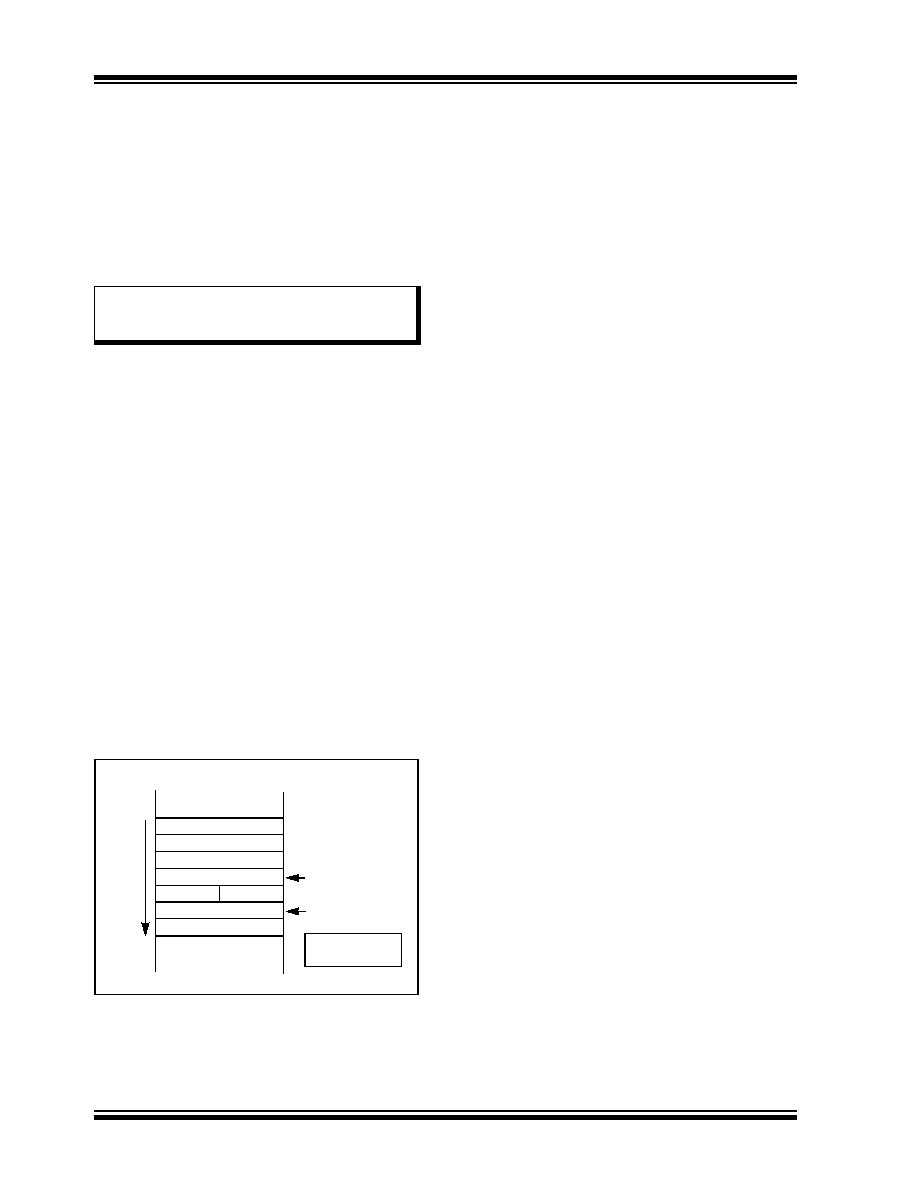
In addition to its use as a working register, the W15 reg-
ister in PIC24F devices is also used as a Software
Stack Pointer. The pointer always points to the first
available free word and grows from lower to higher
addresses. It predecrements for stack pops and post-
increments for stack pushes, as shown in Figure 4-4.
Note that for a PC push during any CALL instruction,
the MSB of the PC is zero-extended before the push,
ensuring that the MSB is always clear.
The Stack Pointer Limit register (SPLIM) associated
with the Stack Pointer sets an upper address boundary
for the stack. SPLIM is uninitialized at Reset. As is the
case for the Stack Pointer, SPLIM<0> is forced to ‘0’
because all stack operations must be word-aligned.
Whenever an EA is generated using W15 as a source
or destination pointer, the resulting address is com-
pared with the value in SPLIM. If the contents of the
Stack Pointer (W15) and the SPLIM register are equal
and a push operation is performed, a stack error trap
will not occur. The stack error trap will occur on a
subsequent push operation. Thus, for example, if it is
desirable to cause a stack error trap when the stack
grows beyond address, 2000h, in RAM, initialize the
SPLIM with the value, 1FFEh.
Similarly, a Stack Pointer underflow (stack error) trap is
generated when the Stack Pointer address is found to
be less than 0800h. This prevents the stack from
interfering with the Special Function Register (SFR)
space.
A write to the SPLIM register should not be immediately
followed by an indirect read operation using W15.
FIGURE 4-4:
CALL
STACK FRAME
4.3
Interfacing Program and Data
Memory Spaces
The PIC24F architecture uses a 24-bit wide program
space and 16-bit wide data space. The architecture is
also a modified Harvard scheme, meaning that data
can also be present in the program space. To use this
data successfully, it must be accessed in a way that
preserves the alignment of information in both spaces.
Aside from normal execution, the PIC24F architecture
provides two methods by which program space can be
accessed during operation:
Using table instructions to access individual bytes
or words anywhere in the program space
Remapping a portion of the program space into
the data space (Program Space Visibility)
Table instructions allow an application to read or write
to small areas of the program memory. This makes the
method ideal for accessing data tables that need to be
updated from time to time. It also allows access to all
bytes of the program word. The remapping method
allows an application to access a large block of data on
a read-only basis, which is ideal for look ups from a
large table of static data. It can only access the least
significant word of the program word.
4.3.1
ADDRESSING PROGRAM SPACE
Since the address ranges for the data and program
spaces are 16 and 24 bits, respectively, a method is
needed to create a 23-bit or 24-bit program address
from 16-bit data registers. The solution depends on the
interface method to be used.
For table operations, the 8-bit Table Page register
(TBLPAG) is used to define a 32K word region within
the program space. This is concatenated with a 16-bit
EA to arrive at a full 24-bit program space address. In
this format, the Most Significant bit of TBLPAG is used
to determine if the operation occurs in the user memory
(TBLPAG<7> = 0) or the configuration memory
(TBLPAG<7> = 1).
For remapping operations, the 8-bit Program Space
Visibility register (PSVPAG) is used to define a
16K word page in the program space. When the Most
Significant bit of the EA is ‘1’, PSVPAG is concatenated
with the lower 15 bits of the EA to form a 23-bit program
space address. Unlike table operations, this limits
remapping operations strictly to the user memory area.
Table 4-31 and Figure 4-5 show how the program EA is
created for table operations and remapping accesses
from the data EA. Here, P<23:0> refers to a program
space word, whereas D<15:0> refers to a data space
word.
Note:
A PC push during exception processing
will concatenate the SRL register to the
MSB of the PC prior to the push.
<Free Word>
PC<15:0>
000000000
0
15
W15 (before CALL)
W15 (after CALL)
S
tac
kG
row
sT
o
w
a
rd
s
Highe
rA
ddr
es
s
0000h
PC<22:16>
POP
: [--W15]
PUSH : [W15++]
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| DSPIC30F2010-20I/MM | IC DSPIC MCU/DSP 12K 28QFN |
| PIC32MX150F128B-I/SO | IC MCU 32BIT 128KB FLASH 28-SOIC |
| PIC32MX230F064B-I/SO | IC MCU 32BIT 64KB FLASH 28-SOIC |
| PIC24FJ32GB002-I/ML | IC MCU 16BIT 32KB FLASH 28QFN |
| PIC16F88-I/ML | IC MCU FLASH 4KX14 EEPROM 28QFN |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| PIC24FJ64GA006T-I/PT | 功能描述:16位微控制器 - MCU 64KB 53 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:RISC 处理器系列:MSP430FR572x 数据总线宽度:16 bit 最大时钟频率:24 MHz 程序存储器大小:8 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 85 C 封装 / 箱体:VQFN-40 安装风格:SMD/SMT |
| PIC24FJ64GA008 | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全称:Microchip Technology 功能描述:General Purpose, 16-Bit Flash Microcontrollers |
| PIC24FJ64GA008-I/PT | 功能描述:16位微控制器 - MCU 64KB 69 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:RISC 处理器系列:MSP430FR572x 数据总线宽度:16 bit 最大时钟频率:24 MHz 程序存储器大小:8 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 85 C 封装 / 箱体:VQFN-40 安装风格:SMD/SMT |
| PIC24FJ64GA008T-I/PT | 功能描述:16位微控制器 - MCU 64KB 69 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 核心:RISC 处理器系列:MSP430FR572x 数据总线宽度:16 bit 最大时钟频率:24 MHz 程序存储器大小:8 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:2 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 85 C 封装 / 箱体:VQFN-40 安装风格:SMD/SMT |
| PIC24FJ64GA010 | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全称:Microchip Technology 功能描述:General Purpose, 16-Bit Flash Microcontrollers |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。