- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录1839 > MAX17030GTL+ (Maxim Integrated Products)IC CTRLR VID QUICK-PWM 40-TQFN PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | MAX17030GTL+ |
| 厂商: | Maxim Integrated Products |
| 文件页数: | 33/39页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC CTRLR VID QUICK-PWM 40-TQFN |
| 产品培训模块: | Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program |
| 标准包装: | 60 |
| 系列: | Quick-PWM™ |
| 应用: | 控制器,Intel IMVP-6.5? SV,XE |
| 输入电压: | 7 V ~ 26 V |
| 输出数: | 1 |
| 输出电压: | 0.013 V ~ 1.5 V |
| 工作温度: | 0°C ~ 85°C |
| 安装类型: | 表面贴装 |
| 封装/外壳: | 40-WFQFN 裸露焊盘 |
| 供应商设备封装: | 40-TQFN-EP(5x5) |
| 包装: | 管件 |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页当前第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页
�� �
�
 �
�1/2/3-Phase� Quick-PWM�
�IMVP-6.5� VID� Controllers�
�?�
�Maximum� load� current:� There� are� two� values� to�
�BST_�
�DH_�
�LX_�
�(R� BST� )*�
�C� BST�
�N� H�
�INPUT� (V� IN� )�
�L�
�consider.� The� peak� load� current� (I� LOAD(MAX)� )� deter-�
�mines� the� instantaneous� component� stresses� and�
�filtering� requirements,� and� thus� drives� output�
�capacitor� selection,� inductor� saturation� rating,� and�
�the� design� of� the� current-limit� circuit.� The� continu-�
�ous� load� current� (I� LOAD� )� determines� the� thermal�
�stresses� and� thus� drives� the� selection� of� input�
�I� LOAD� (� PHASE� )� =� LOAD�
�V� DD�
�DL_�
�PGND�
�MAX17030/MAX17036�
�C� BYP�
�(C� NL� )*�
�N� L�
�capacitors,� MOSFETs,� and� other� critical� heat-con-�
�tributing� components.� Modern� notebook� CPUs� gen-�
�erally� exhibit� I� LOAD� =� I� LOAD(MAX)� x� 80%.�
�For� multiphase� systems,� each� phase� supports� a�
�fraction� of� the� load,� depending� on� the� current� bal-�
�ancing.� When� properly� balanced,� the� load� current� is�
�evenly� distributed� among� each� phase:�
�I�
�η� TOTAL�
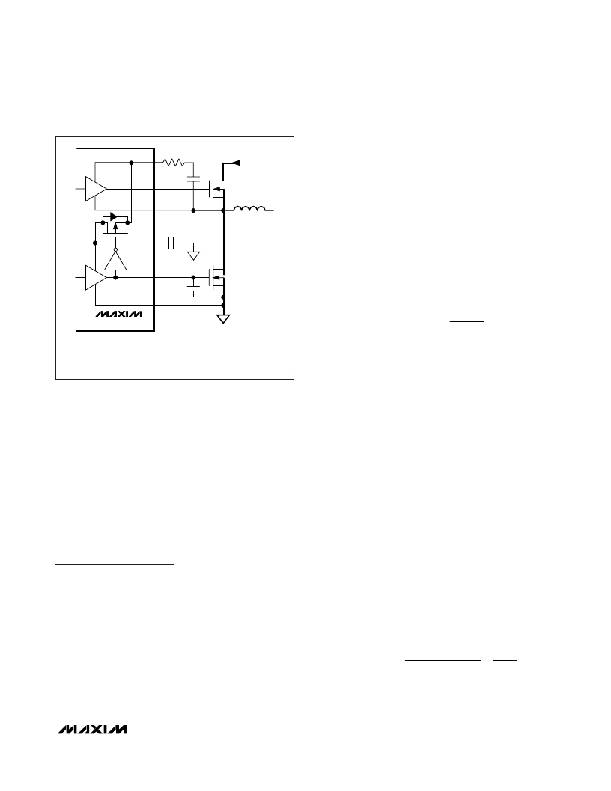
�(R� BST� )*� OPTIONAL—THE� RESISTOR� LOWERS� EMI� BY� DECREASING� THE�
�SWITCHING� NODE� RISE� TIME.�
�(C� NL� )*� OPTIONAL—THE� CAPACITOR� REDUCES� LX� TO� DL� CAPACITIVE�
�COUPLING� THAT� CAN� CAUSE� SHOOT-THROUGH� CURRENT.�
�Figure� 10.� Gate� Drive� Circuit�
�Shoot-through� currents� can� also� be� caused� by� a� com-�
�bination� of� fast� high-side� MOSFETs� and� slow� low-side�
�MOSFETs.� If� the� turn-off� delay� time� of� the� low-side�
�MOSFET� is� too� long,� the� high-side� MOSFETs� can� turn�
�on� before� the� low-side� MOSFETs� have� actually� turned�
�off.� Adding� a� resistor� less� than� 5� Ω� in� series� with� BST�
�slows� down� the� high-side� MOSFET� turn-on� time,� elimi-�
�nating� the� shoot-through� currents� without� degrading� the�
�turn-off� time� (R� BST� in� Figure� 10).� Slowing� down� the�
�high-side� MOSFET� also� reduces� the� LX� node� rise� time,�
�thereby� reducing� EMI� and� high-frequency� coupling�
�responsible� for� switching� noise.�
�?�
�?�
�where� η� TOTAL� is� the� total� number� of� active� phases.�
�Switching� frequency:� This� choice� determines� the�
�basic� trade-off� between� size� and� efficiency.� The�
�optimal� frequency� is� largely� a� function� of� maximum�
�input� voltage,� due� to� MOSFET� switching� losses� that�
�are� proportional� to� frequency� and� V� IN� 2� .� The� opti-�
�mum� frequency� is� also� a� moving� target,� due� to�
�rapid� improvements� in� MOSFET� technology� that� are�
�making� higher� frequencies� more� practical.�
�Inductor� operating� point:� This� choice� provides�
�trade-offs� between� size� vs.� efficiency� and� transient�
�response� vs.� output� noise.� Low� inductor� values� pro-�
�vide� better� transient� response� and� smaller� physical�
�size,� but� also� result� in� lower� efficiency� and� higher�
�output� noise� due� to� increased� ripple� current.� The�
�minimum� practical� inductor� value� is� one� that� causes�
�the� circuit� to� operate� at� the� edge� of� critical� conduc-�
�Multiphase� Quick-PWM�
�Design� Procedure�
�Firmly� establish� the� input� voltage� range� and� maximum�
�load� current� before� choosing� a� switching� frequency� and�
�inductor� operating� point� (ripple-current� ratio).� The� pri-�
�mary� design� trade-off� lies� in� choosing� a� good� switching�
�frequency� and� inductor� operating� point,� and� the� following�
�four� factors� dictate� the� rest� of� the� design:�
�tion� (where� the� inductor� current� just� touches� zero�
�with� every� cycle� at� maximum� load).� Inductor� values�
�lower� than� this� grant� no� further� size-reduction� bene-�
�fit.� The� optimum� operating� point� is� usually� found�
�between� 30%� and� 50%� ripple� current.� for� a� multi-�
�phase� core� regulator,� select� an� LIR� value� of� ~0.4.�
�Inductor� Selection�
�The� switching� frequency� and� operating� point� (%� ripple�
�current� or� LIR)� determine� the� inductor� value� as� follows:�
�V� IN� ?� V� OUT�
�L� =� η� TOTAL� ?� ?� ?� ?�
�?� f� SW� LOAD� (� MAX� )� LIR� ?� ?� V� I� N� ?�
�?�
�Input� voltage� range:� The� maximum� value�
�(V� IN(MAX)� )� must� accommodate� the� worst-case� high�
�AC� adapter� voltage.� The� minimum� value� (V� IN(MIN)� )�
�must� account� for� the� lowest� input� voltage� after�
�drops� due� to� connectors,� fuses,� and� battery� selec-�
�tor� switches.� If� there� is� a� choice� at� all,� lower� input�
�voltages� result� in� better� efficiency.�
�?� ?� ?� V� OUT� ?�
�I�
�where� η� TOTAL� is� the� total� number� of� phases.�
�______________________________________________________________________________________�
�33�
�相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX1703ESE | IC REG BOOST SYNC 5V/ADJ 16SOIC |
| MAX17041G+T | IC 2-WIRE FG W/MODEL GAUGE |
| MAX17044G+T | IC FUEL GAUGE LI-ION 8-TDFN |
| MAX17049G+ | IC FUEL/GAS GAUGE LI-ION 8TDFN |
| MAX17062ETB+T | IC TFT-LCD DC/DC CONV 10-TDFN |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| MAX17030GTL+ | 功能描述:电压模式 PWM 控制器 1/2/3-Phase PWM IMVP-6.5 VID Ctlr RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 输出端数量:1 拓扑结构:Buck 输出电压:34 V 输出电流: 开关频率: 工作电源电压:4.5 V to 5.5 V 电源电流:600 uA 最大工作温度:+ 125 C 最小工作温度:- 40 C 封装 / 箱体:WSON-8 封装:Reel |
| MAX17030GTL+T | 功能描述:电压模式 PWM 控制器 1/2/3-Phase PWM IMVP-6.5 VID Ctlr RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 输出端数量:1 拓扑结构:Buck 输出电压:34 V 输出电流: 开关频率: 工作电源电压:4.5 V to 5.5 V 电源电流:600 uA 最大工作温度:+ 125 C 最小工作温度:- 40 C 封装 / 箱体:WSON-8 封装:Reel |
| MAX17031ETG+ | 功能描述:电压模式 PWM 控制器 Dual PWM Step-Down Controller RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 输出端数量:1 拓扑结构:Buck 输出电压:34 V 输出电流: 开关频率: 工作电源电压:4.5 V to 5.5 V 电源电流:600 uA 最大工作温度:+ 125 C 最小工作温度:- 40 C 封装 / 箱体:WSON-8 封装:Reel |
| MAX17031ETG+T | 功能描述:电压模式 PWM 控制器 Dual PWM Step-Down Controller RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 输出端数量:1 拓扑结构:Buck 输出电压:34 V 输出电流: 开关频率: 工作电源电压:4.5 V to 5.5 V 电源电流:600 uA 最大工作温度:+ 125 C 最小工作温度:- 40 C 封装 / 箱体:WSON-8 封装:Reel |
| MAX17033GTL+ | 功能描述:电压模式 PWM 控制器 Dual PWM Step-Down Controller RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 输出端数量:1 拓扑结构:Buck 输出电压:34 V 输出电流: 开关频率: 工作电源电压:4.5 V to 5.5 V 电源电流:600 uA 最大工作温度:+ 125 C 最小工作温度:- 40 C 封装 / 箱体:WSON-8 封装:Reel |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。