- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录11599 > MCP2140-I/SO (Microchip Technology)IC IRDA CONTROLLR DTE/DCE 18SOIC PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | MCP2140-I/SO |
| 厂商: | Microchip Technology |
| 文件页数: | 46/58页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC IRDA CONTROLLR DTE/DCE 18SOIC |
| 产品培训模块: | IrDA® Standard Protocol |
| 标准包装: | 42 |
| 控制器类型: | IRDA 标准协议栈控制器 |
| 接口: | UART |
| 电源电压: | 3 V ~ 5.5 V |
| 电流 - 电源: | 2.2mA |
| 工作温度: | -40°C ~ 125°C |
| 安装类型: | 表面贴装 |
| 封装/外壳: | 18-SOIC(0.295",7.50mm 宽) |
| 供应商设备封装: | 18-SOIC |
| 包装: | 管件 |
| 产品目录页面: | 685 (CN2011-ZH PDF) |
| 配用: | MCP2140DM-TMPSNS-ND - BOARD DEMO FOR MCP2140 |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页当前第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页
MCP2140
DS21790A-page 50
Preliminary
2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
APPENDIX C: HOW DEVICES
CONNECT
When two devices implementing the IrDA standard fea-
ture establish a connection using the IrCOMM protocol,
the process is analogous to connecting two devices
with serial ports using a cable. This is referred to as a
“point-to-point” connection. This connection is limited
to half-duplex operation because the IR transceiver
cannot transmit and receive at the same time. The pur-
pose of the IrDA protocols is to allow this half-duplex
link to emulate, as much as possible, a full-duplex con-
nection. In general, this is done by dividing the data into
“packets”, or groups of data. These packets can then
be sent back and forth, when needed, without risk of
collision. The rules of how and when these packets are
sent constitute the IrDA protocols.
When a wired connection is used, the assumption is
made that both sides have the same communications
parameters and features. A wired connection has no
need to identify the other connector because it is
assumed that the connectors are properly connected.
In the IrDA standard, a connection process has been
defined to identify other IrDA compatible devices and
establish a communication link. There are three steps
that these two devices go through to make this
connection. They are:
Normal Disconnect Mode (NDM)
Discovery Mode
Normal Connect Mode (NCM)
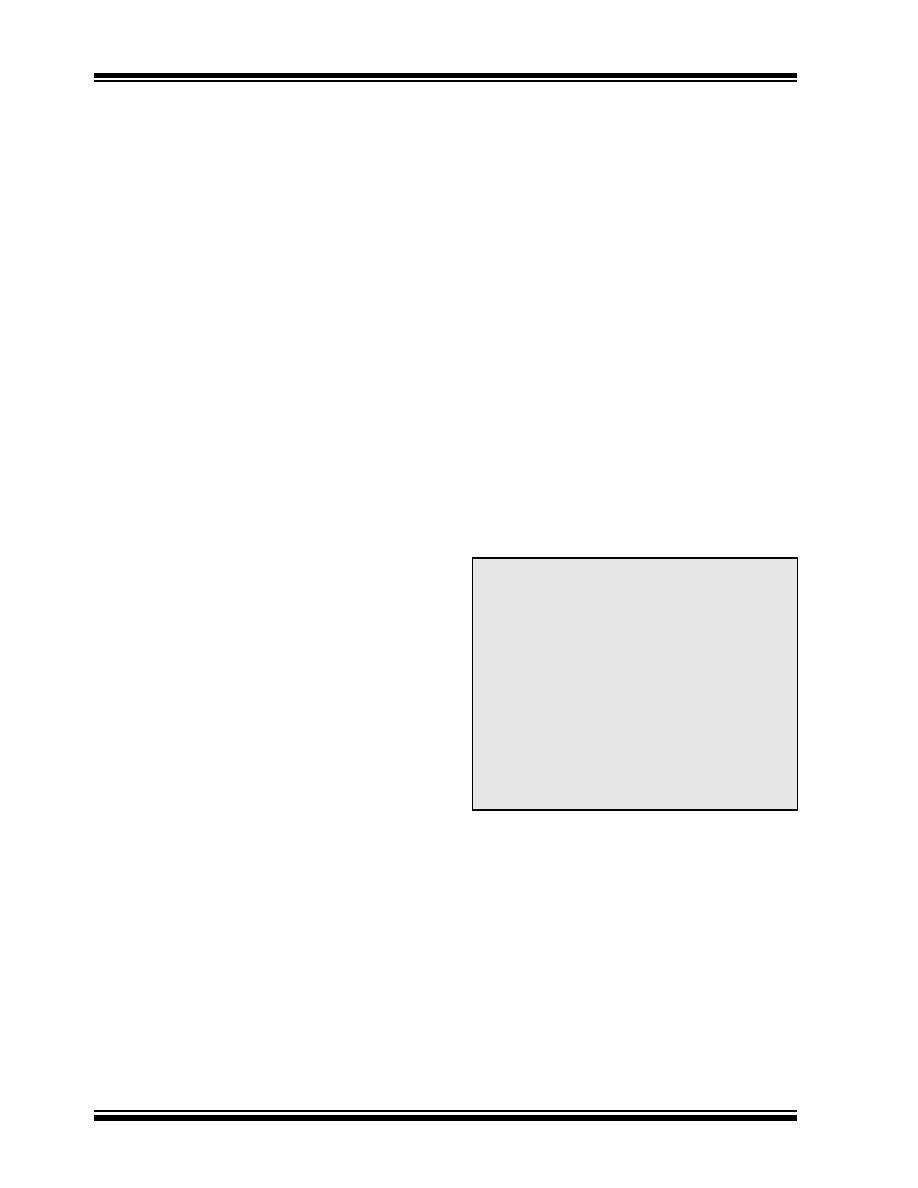
Figure C-1 shows the connection sequence.
C.1
Normal Disconnect Mode (NDM)
When two IrDA standard compatible devices come into
range they must first recognize each other. The basis
of this process is that one device has some task to
accomplish and the other device has a resource
needed to accomplish this task. One device is referred
to as a Primary device and the other is referred to as a
Secondary device. This distinction between Primary
device and Secondary device is important. It is the
responsibility of the Primary device to provide the
mechanism to recognize other devices. So the Primary
device must first poll for nearby IrDA standard compat-
ible devices. During this polling, the default baud rate of
9600 baud is used by both devices.
For example, if you want to print from an IrDA equipped
laptop to an IrDA printer, utilizing the IrDA standard fea-
ture, you would first bring your laptop in range of the
printer. In this case, the laptop is the one that has
something to do and the printer has the resource to do
it. The laptop is called the Primary device and the
printer is the Secondary device. Some data-capable
cell phones have IrDA standard infrared ports. If you
used such a cell phone with a Personal Digital Assis-
tant (PDA), the PDA that supports the IrDA standard
feature would be the Primary device and the cell phone
would be the Secondary device.
When a Primary device polls for another device, a
nearby Secondary device may respond. When a Sec-
ondary device responds, the two devices are defined to
be in the Normal Disconnect Mode (NDM) state. NDM
is established by the Primary device broadcasting a
packet and waiting for a response. These broadcast
packets are numbered. Usually 6 or 8 packets are sent.
The first packet is number 0, the last packet is usually
number 5 or 7. Once all the packets are sent, the Pri-
mary device sends an ID packet, which is not num-
bered.
The Secondary device waits for these packets and then
responds to one of the packets. The packet responds
to determines the “timeslot” to be used by the Second-
ary device. For example, if the Secondary device
responds after packet number 2, then the Secondary
device will use timeslot 2. If the Secondary device
responds after packet number 0, then the Secondary
device will use timeslot 0. This mechanism allows the
Primary device to recognize as many nearby devices
as there are timeslots. The Primary device will continue
to generate timeslots and the Secondary device should
continue to respond, even if there’s nothing to do.
Note 1: The MCP2140 can only be used to
implement a Secondary device.
2: The MCP2140 supports a system with
only one Secondary device having exclu-
sive use of the IrDA standard infrared link
(known as “point-to-point” communica-
tion).
3: The MCP2140 always responds to packet
number 2. This means that the MCP2140
will always use timeslot 2.
4: If another Secondary device is nearby,
the Primary device may fail to recognize
the MCP2140, or the Primary device may
not recognize either of the devices.
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ENC28J60T-I/SO | IC ETHERNET CTRLR W/SPI 28-SOIC |
| ENC28J60T-I/SS | IC ETHERNET CTLR SPI 28SSOP |
| GRM21BF51C225ZA01K | CAP CER 2.2UF 16V Y5V 0805 |
| GRM21BF51A225ZA01K | CAP CER 2.2UF 10V Y5V 0805 |
| MCP2140A-I/SS | IC IRDA CONTROLLR DTE/DCE 20SSOP |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| MCP2140-ISS | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全称:Microchip Technology 功能描述:IrDA㈢ Standard Protocol Stack Controller With Fixed 9600 Baud Communication Rate |
| MCP2140T-I/SO | 功能描述:网络控制器与处理器 IC 9600bd fixd spd IrDA RoHS:否 制造商:Micrel 产品:Controller Area Network (CAN) 收发器数量: 数据速率: 电源电流(最大值):595 mA 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:PBGA-400 封装:Tray |
| MCP2140T-I/SS | 功能描述:网络控制器与处理器 IC 9600bd fixd spd IrDA RoHS:否 制造商:Micrel 产品:Controller Area Network (CAN) 收发器数量: 数据速率: 电源电流(最大值):595 mA 最大工作温度:+ 85 C 安装风格:SMD/SMT 封装 / 箱体:PBGA-400 封装:Tray |
| MCP2140T-IP | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全称:Microchip Technology 功能描述:IrDA㈢ Standard Protocol Stack Controller With Fixed 9600 Baud Communication Rate |
| MCP2140T-ISO | 制造商:MICROCHIP 制造商全称:Microchip Technology 功能描述:IrDA㈢ Standard Protocol Stack Controller With Fixed 9600 Baud Communication Rate |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。