- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录367742 > P89C662HFA (NXP SEMICONDUCTORS) 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | P89C662HFA |
| 厂商: | NXP SEMICONDUCTORS |
| 元件分类: | 微控制器/微处理器 |
| 英文描述: | 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
| 中文描述: | 8-BIT, FLASH, 33 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQCC44 |
| 封装: | PLASTIC, MS-018, SOT-187-2, LCC-44 |
| 文件页数: | 7/89页 |
| 文件大小: | 491K |
| 代理商: | P89C662HFA |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页当前第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页
Philips Semiconductors
Product data
P89C660/P89C662/P89C664/
P89C668
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
16KB/32KB/64KB ISP/IAP Flash with 512B/1KB/2KB/8KB RAM
2002 Oct 28
7
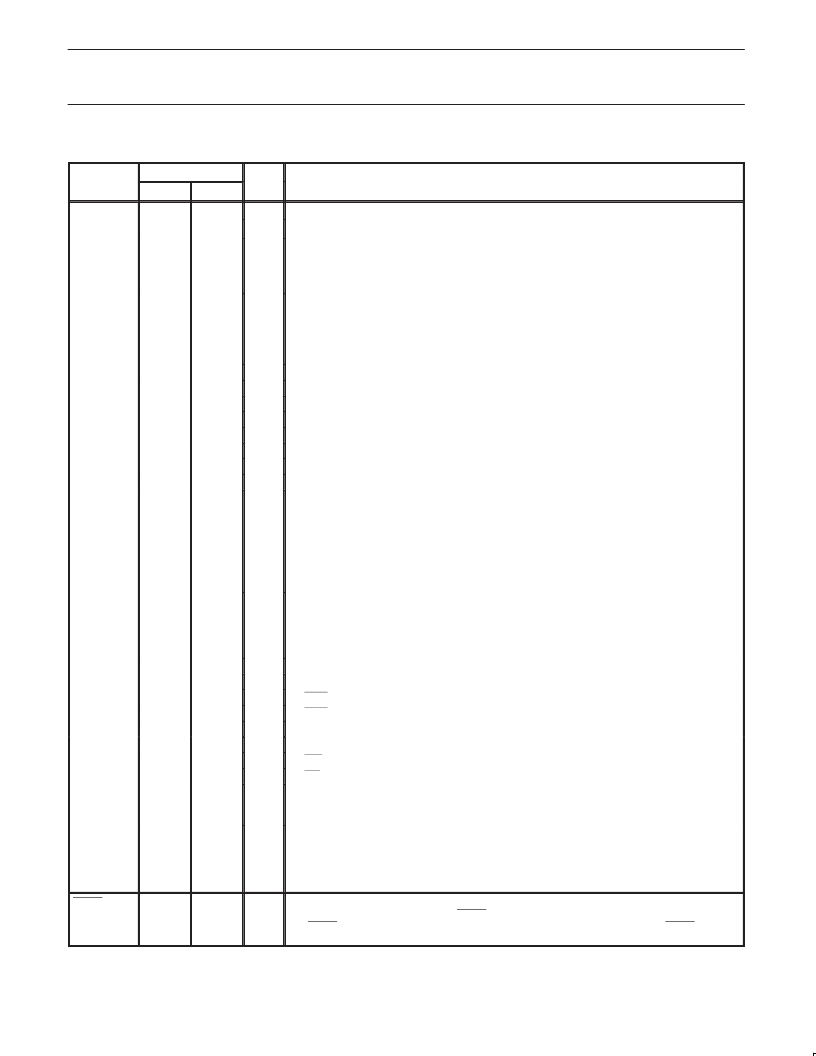
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
MNEMONIC
PIN NUMBER
TYPE
NAME AND FUNCTION
PLCC
LQFP
V
SS
V
CC
P0.0–0.7
22
16
I
Ground:
0 V reference.
44
38
I
Power Supply:
This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power-down operation.
43–36
37–30
I/O
Port 0:
Port 0 is an open-drain, bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to them
float and can be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed low-order
address and data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In this
application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s.
P1.0–P1.7
2–9
40–44,
1–3
I/O
Port 1:
Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups on all pins except P1.6 and
P1.7 which are open drain. Port 1 pins that have 1s written to them are pulled high by the
internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 1 pins that are externally pulled low
will source current because of the internal pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
).
Alternate functions for P89C660/662/664/668 Port 1 include:
T2 (P1.0):
Timer/Counter 2 external count input/Clockout (see Programmable Clock-Out)
T2EX (P1.1):
Timer/Counter 2 Reload/Capture/Direction Control
ECI (P1.2):
External Clock Input to the PCA
CEX0 (P1.3):
Capture/Compare External I/O for PCA module 0
CEX1 (P1.4):
Capture/Compare External I/O for PCA module 1
CEX2 (P1.5):
Capture/Compare External I/O for PCA module 2
SCL (P1.6):
I
2
C bus clock line (open drain)
SDA (P1.7):
I
2
C bus data line (open drain)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
40
41
42
43
44
1
2
3
I/O
I
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
P2.0–P2.7
24–31
18–25
I/O
Port 2:
Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the internal
pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
). Port 2 emits the high-order address byte
during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to external data memory
that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups
when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit addresses (MOV
@Ri), port 2 emits the contents of the P2 special function register.
P3.0–P3.7
11,
13–19
5, 7–13
I/O
Port 3:
Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the pull-ups. (See
DC Electrical Characteristics: I
). Port 3 also serves the special features of the
P89C660/662/664/668, as listed below:
RxD (P3.0):
Serial input port
TxD (P3.1):
Serial output port
INT0 (P3.2):
External interrupt
INT1 (P3.3):
External interrupt
CEX3/T0 (P3.4):
Timer 0 external input; Capture/Compare External I/O for PCA module 3
CEX4/T1 (P3.5):
Timer 1 external input; Capture/Compare External I/O for PCA module 4
WR (P3.6):
External data memory write strobe
RD (P3.7):
External data memory read strobe
11
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
5
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
I
O
I
I
I
I
O
O
RST
10
4
I
Reset:
A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running, resets the
device. An internal resistor to V
SS
permits a power-on reset using only an external capacitor to
V
CC
.
Address Latch Enable:
Output pulse for latching the low byte of the address during an access
to external memory. In normal operation, ALE is emitted twice every machine cycle, and can be
used for external timing or clocking. Note that one ALE pulse is skipped during each access to
external data memory. ALE can be disabled by setting SFR auxiliary.0. With this bit set, ALE
will be active only during a MOVX instruction.
ALE
33
27
O
PSEN
32
26
O
Program Store Enable:
The read strobe to external program memory. When executing code
from the external program memory, PSEN is activated twice each machine cycle, except that
two PSEN activations are skipped during each access to external data memory. PSEN is not
activated during fetches from internal program memory.
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| P89C662HFBD | 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
| P89C664 | 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
| P89C664HFA | 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
| P89C664HFBD | 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
| P89C662HBA | 80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| P89C662HFA/00,512 | 功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 32K/1K FL 6 CLK ISP/IAP IND RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT |
| P89C662HFBD | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全称:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
| P89C662HFBD/00,557 | 功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 32K/1K FL 6CLK ISP/IAP QFP IND RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT |
| P89C664 | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全称:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:On-chip Flash 8-bit microcontroller Errata Sheet |
| P89C664HBA | 制造商:PHILIPS 制造商全称:NXP Semiconductors 功能描述:80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。