- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录9301 > AD5203ARUZ10-REEL (Analog Devices Inc)IC POT DGTL QUAD 64POS 24TSSOP PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | AD5203ARUZ10-REEL |
| 厂商: | Analog Devices Inc |
| 文件页数: | 12/12页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC POT DGTL QUAD 64POS 24TSSOP |
| 标准包装: | 2,500 |
| 接片: | 64 |
| 电阻(欧姆): | 10k |
| 电路数: | 4 |
| 温度系数: | 标准值 700 ppm/°C |
| 存储器类型: | 易失 |
| 接口: | 4 线 SPI(芯片选择) |
| 电源电压: | 2.7 V ~ 5.5 V |
| 工作温度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 安装类型: | 表面贴装 |
| 封装/外壳: | 24-TSSOP(0.173",4.40mm 宽) |
| 供应商设备封装: | 24-TSSOP |
| 包装: | 带卷 (TR) |
AD5203
–9–
REV. 0
OPERATION
The AD5203 provides a quad channel, 64-position digitally-
controlled variable resistor (VR) device. Changing the pro-
grammed VR settings is accomplished by clocking in an 8-bit
serial data word into the SDI (Serial Data Input) pin. The for-
mat of this data word is two address bits, MSB first, followed by
six data bits, MSB first. Table I provides the serial register data
word format. The AD5203 has the following address assign-
ments for the ADDR decode, which determines the location of
VR latch receiving the serial register data in Bits B5 through B0:
VR# = A1
× 2 + A0 + 1
VR outputs can be changed one at a time in random sequence.
The serial clock running at 10 MHz makes it possible to load all
four VRs in under 3.2
s (8 × 4 × 100 ns) for the AD5203. The
exact timing requirements are shown in Figure 1.
The AD5203 resets to a midscale by asserting the
RS pin, sim-
plifying initial conditions at power-up. Both parts have a power
shutdown
SHDN pin that places the RDAC in a zero power
consumption state where terminals Ax are open-circuited and
the wiper Wx is connected to Bx, resulting in only leakage cur-
rents being consumed in the VR structure. In shutdown mode
the VR latch settings are maintained so that, returning to opera-
tional mode from power shutdown, the VR settings return to
their previous resistance values.
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
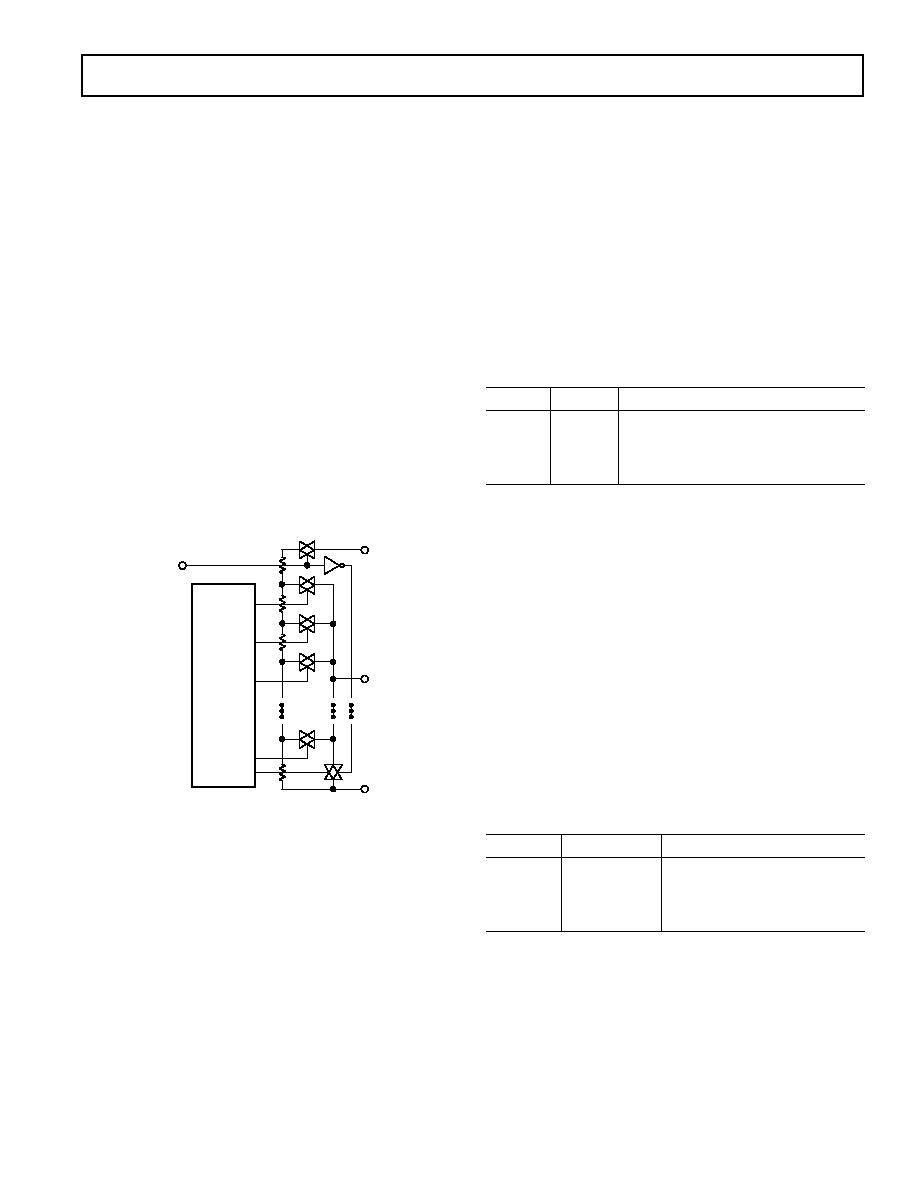
D0
RDAC
LATCH
&
DECODER
Ax
Wx
Bx
RS = RAB/64
RS
SHDN
Figure 34. Equivalent RDAC Circuit
PROGRAMMING THE VARIABLE RESISTOR
Rheostat Operation
The nominal resistance of the RDAC between Terminals A and
B are available with values of 10 k
, and 100 k. The final
digits of the part number determine the nominal resistance
value, e.g., 10 k
= 10; 100 k = 100. The nominal resistance
(RAB) of the VR has 64 contact points accessed by the wiper
terminal, plus the B terminal contact. The 6-bit data word in
the RDAC latch is decoded to select one of the 64 possible
settings. The wiper’s first connection starts at the B terminal for
data 00H. This B–terminal connection has a wiper contact resis-
tance of 45
. The second connection (10 k part) is the first
tap point located at 201
[= R
BA(nominal resistance)/64 + RW
= 156
+ 45 )] for data 01
H. The third connection is the next
tap point representing 312 + 45 = 357
for data 02
H. Each
LSB data value increase moves the wiper up the resistor ladder
until the last tap point is reached at 9889
. The wiper does not
directly connect to the B Terminal. See Figure 34 for a simpli-
fied diagram of the equivalent RDAC circuit.
The general transfer equation that determines the digitally pro-
grammed output resistance between Wx and Bx is:
RWB(Dx) = (Dx)/64
× R
BA + RW
(1)
where Dx is the data contained in the 6-bit RDACx latch and
RBA is the nominal end-to-end resistance.
For example, when VB = 0 V and A–terminal is open circuit the
following output resistance values will be set for the following
RDAC latch codes (applies to the 10K potentiometer):
D (DEC) RWB ( )
Output State
63
9889
Full-Scale
32
5045
Midscale (
RS = 0 Condition)
1
201
1 LSB
0
45
Zero-Scale (Wiper Contact Resistance)
Note that in the zero-scale condition a finite wiper resistance of
45
is present. Care should be taken to limit the current flow
between W and B in this state to a maximum value of 5 mA to
avoid degradation or possible destruction of the internal switch
contact.
Like the mechanical potentiometer the RDAC replaces, it is
totally symmetrical. The resistance between the wiper W and
terminal A also produces a digitally controlled resistance RWA.
When these terminals are used the B–terminal should be tied to
the wiper. Setting the resistance value for RWA starts at a maxi-
mum value of resistance and decreases as the data loaded in the
latch is increased in value. The general transfer equation for this
operation is:
RWA(Dx) = (64-Dx)/64
× R
BA + RW
(2)
where Dx is the data contained in the 6-bit RDACx latch and
RBA is the nominal end-to-end resistance. For example, when
VA = 0 V and B–terminal is tied to the wiper W, the following
output resistance values will be set for the following RDAC
latch codes:
D (DEC)
RWA ( )
Output State
63
201
Full-Scale
32
5045
Midscale (
RS = 0 Condition)
1
9889
1 LSB
0
10045
Zero-Scale
The typical distribution of RBA from channel to channel matches
within
±1%. However, device-to-device matching is process-lot-
dependent, having a
±30% variation. The change in R
BA with
temperature has a 700 ppm/
°C temperature coefficient.
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| LTC6994IDCB-2#TRPBF | IC DELAY LINE 6-DFN |
| VI-BNB-IU-F4 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 95V 200W |
| LTC6994IDCB-2#TRMPBF | IC DELAY LINE 6-DFN |
| VI-BNB-IU-F3 | CONVERTER MOD DC/DC 95V 200W |
| AD8400ARZ1-REEL | IC POT DGTL 8BIT SGL 1K 8SOIC |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| AD5203ARZ10 | 功能描述:IC POT DGTL QUAD 64POS 24SOIC RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 数字电位器 系列:- 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:1 系列:- 接片:256 电阻(欧姆):100k 电路数:1 温度系数:标准值 35 ppm/°C 存储器类型:非易失 接口:3 线串口 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.25 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:8-WDFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:8-TDFN-EP(3x3) 包装:剪切带 (CT) 产品目录页面:1399 (CN2011-ZH PDF) 其它名称:MAX5423ETA+TCT |
| AD5203ARZ100 | 功能描述:IC POT DGTL QUAD 64POS 24SOIC RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 数字电位器 系列:- 标准包装:2,500 系列:XDCP™ 接片:256 电阻(欧姆):100k 电路数:1 温度系数:标准值 ±300 ppm/°C 存储器类型:非易失 接口:I²C(设备位址) 电源电压:2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:14-TSSOP(0.173",4.40mm 宽) 供应商设备封装:14-TSSOP 包装:带卷 (TR) |
| AD5203ARZ100-REEL | 功能描述:IC POT DGTL QUAD 64POS 24SOIC RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 数据采集 - 数字电位器 系列:- 标准包装:3,000 系列:DPP 接片:32 电阻(欧姆):10k 电路数:1 温度系数:标准值 300 ppm/°C 存储器类型:非易失 接口:3 线串行(芯片选择,递增,增/减) 电源电压:2.5 V ~ 6 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:8-WFDFN 裸露焊盘 供应商设备封装:8-TDFN(2x3) 包装:带卷 (TR) |
| AD5204 | 制造商:AD 制造商全称:Analog Devices 功能描述:256-Position and 33-Position Digital Potentiometers |
| AD5204_10 | 制造商:AD 制造商全称:Analog Devices 功能描述:4-/6-Channel Digital Potentiometers |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。