- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录80565 > MC68HLC908QT1FQ (FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC) 8-BIT, FLASH, 2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQCC8 PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | MC68HLC908QT1FQ |
| 厂商: | FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分类: | 微控制器/微处理器 |
| 英文描述: | 8-BIT, FLASH, 2 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQCC8 |
| 封装: | DFN-8 |
| 文件页数: | 112/186页 |
| 文件大小: | 2765K |
| 代理商: | MC68HLC908QT1FQ |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页第90页第91页第92页第93页第94页第95页第96页第97页第98页第99页第100页第101页第102页第103页第104页第105页第106页第107页第108页第109页第110页第111页当前第112页第113页第114页第115页第116页第117页第118页第119页第120页第121页第122页第123页第124页第125页第126页第127页第128页第129页第130页第131页第132页第133页第134页第135页第136页第137页第138页第139页第140页第141页第142页第143页第144页第145页第146页第147页第148页第149页第150页第151页第152页第153页第154页第155页第156页第157页第158页第159页第160页第161页第162页第163页第164页第165页第166页第167页第168页第169页第170页第171页第172页第173页第174页第175页第176页第177页第178页第179页第180页第181页第182页第183页第184页第185页第186页
Memory
Random-Access Memory (RAM)
MC68HLC908QY/QT Family — Rev. 2
Data Sheet
MOTOROLA
Memory
31
.
2.5 Random-Access Memory (RAM)
The 128 bytes of random-access memory (RAM) are located at addresses
$0080–$00FF. The location of the stack RAM is programmable. The 16-bit stack
pointer allows the stack to be anywhere in the 64-Kbyte memory space.
NOTE:
For correct operation, the stack pointer must point only to RAM locations.
Before processing an interrupt, the central processor unit (CPU) uses five bytes of
the stack to save the contents of the CPU registers.
NOTE:
For M6805, M146805, and M68HC05 compatibility, the H register is not stacked.
During a subroutine call, the CPU uses two bytes of the stack to store the return
address. The stack pointer decrements during pushes and increments during pulls.
NOTE:
Be careful when using nested subroutines. The CPU may overwrite data in the
RAM during a subroutine or during the interrupt stacking operation.
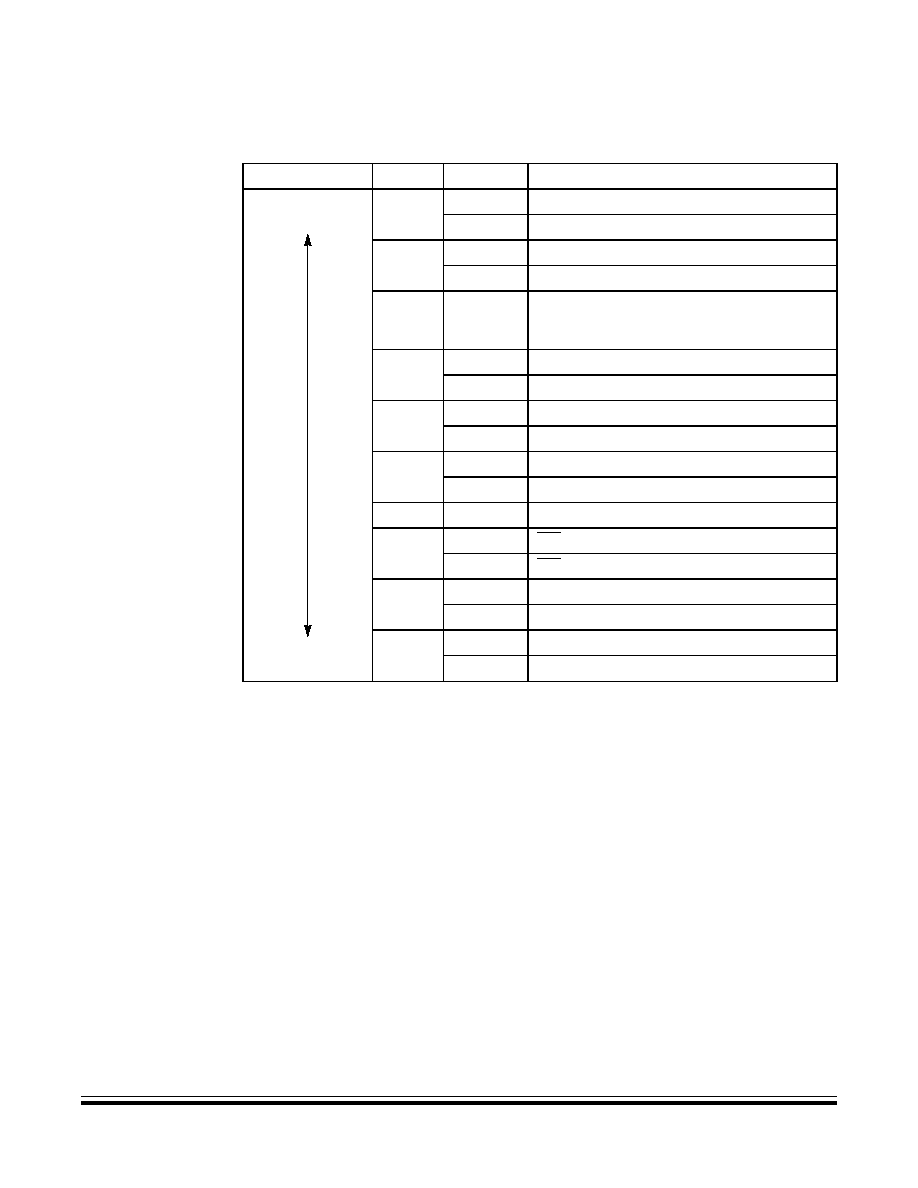
Table 2-1. Vector Addresses
Vector Priority
Vector
Address
Vector
Lowest
Highest
IF15
$FFDE
ADC conversion complete vector (high)
$FFDF
ADC conversion complete vector (low)
IF14
$FFE0
Keyboard vector (high)
$FFE1
Keyboard vector (low)
IF13
↓
IF6
—
Not used
IF5
$FFF2
TIM overflow vector (high)
$FFF3
TIM overflow vector (low)
IF4
$FFF4
TIM Channel 1 vector (high)
$FFF5
TIM Channel 1 vector (low)
IF3
$FFF6
TIM Channel 0 vector (high)
$FFF7
TIM Channel 0 vector (low)
IF2
—
Not used
IF1
$FFFA
IRQ vector (high)
$FFFB
IRQ vector (low)
—
$FFFC
SWI vector (high)
$FFFD
SWI vector (low)
—
$FFFE
Reset vector (high)
$FFFF
Reset vector (low)
F
re
e
sc
a
le
S
e
m
ic
o
n
d
u
c
to
r,
I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
n
c
..
.
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC56F8346MFV60 | 16-BIT, 120 MHz, OTHER DSP, PQFP144 |
| MC68020RP25 | 32-BIT, 25 MHz, MICROPROCESSOR, PPGA114 |
| MC9328MX1DVH20 | 200 MHz, RISC PROCESSOR, PBGA256 |
| MC68HC705J1AVDW | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 2.1 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDSO20 |
| MC68HC908EY16MFA | 8-BIT, FLASH, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP32 |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68HLC908QT4CDW | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68HLC908QT4CFQ | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
| MC68HLC908QY1CDW | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:LOW V-1.5K FLASH W/O ADC - Bulk |
| MC68HLC908QY1DT | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Tape and Reel |
| MC68HLC908QY2CDT | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述:- Bulk |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。