- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Datasheet目录328 > IDT7034L20PFI (IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc)IC SRAM 72KBIT 20NS 100TQFP Datasheet资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | IDT7034L20PFI |
| 厂商: | IDT, Integrated Device Technology Inc |
| 文件页数: | 16/19页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC SRAM 72KBIT 20NS 100TQFP |
| 标准包装: | 3 |
| 格式 - 存储器: | RAM |
| 存储器类型: | SRAM - 双端口,异步 |
| 存储容量: | 72K(4K x 18) |
| 速度: | 20ns |
| 接口: | 并联 |
| 电源电压: | 4.5 V ~ 5.5 V |
| 工作温度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 封装/外壳: | 100-LQFP |
| 供应商设备封装: | 100-TQFP(14x14) |
| 包装: | 托盘 |
| 其它名称: | 7034L20PFI |
�� �
�
 �
�IDT7034S/L�
�High-Speed� 4K� x� 18� Dual-Port� Static� RAM�
�BUSY� LOGIC�
�Industrial� and� Commercial� Temperature� Ranges�
�Busy� Logic� provides� a� hardware� indication� that� both� ports� of� the�
�RAM� have� accessed� the� same� location� at� the� same� time.� It� also� allows�
�one� of� the� two� accesses� to� proceed� and� signals� the� other� side� that� the�
�RAM� is� “busy”.� The� BUSY� pin� can� then� be� used� to� stall� the� access� until�
�the� operation� on� the� other� side� is� completed.� If� a� write� operation� has�
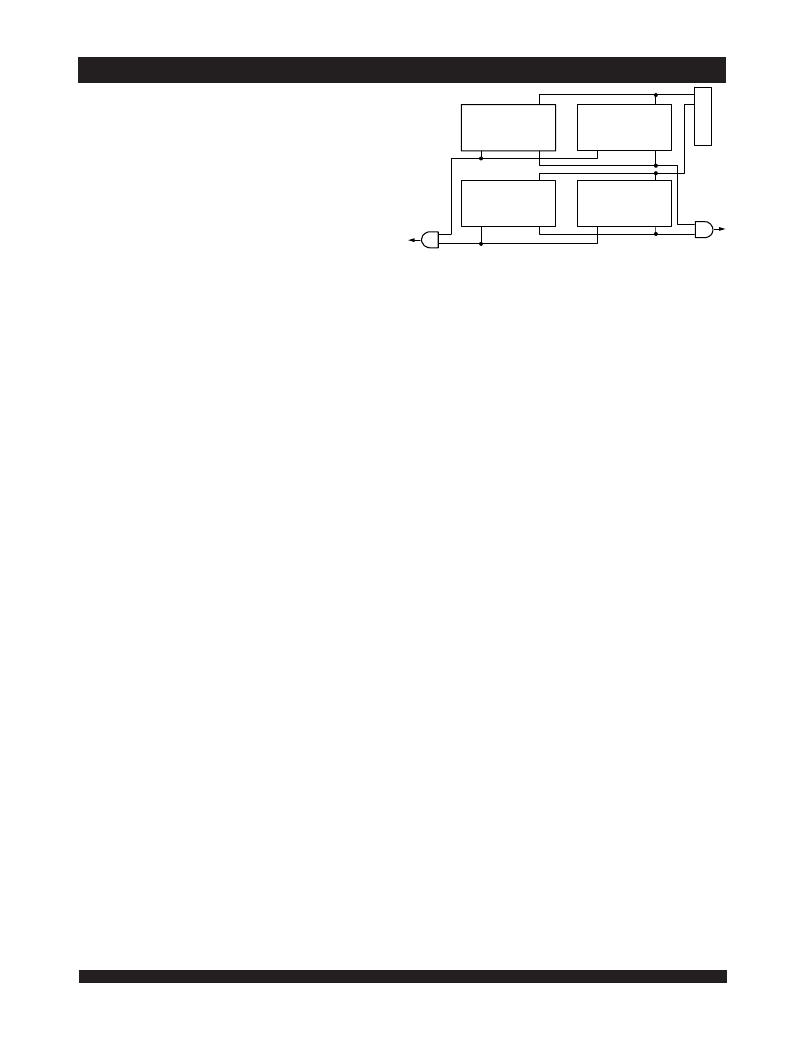
�MASTER� CE�
�Dual� Port�
�RAM�
�BUSY� (L)� BUSY� (R)�
�SLAVE� CE�
�Dual� Port�
�RAM�
�BUSY� (L)� BUSY� (R)�
�been� attempted� from� the� side� that� receives� a� BUSY� indication,� the�
�write� signal� is� gated� internally� to� prevent� the� write� from� proceeding.�
�The� use� of� BUSY� logic� is� not� required� or� desirable� for� all� applica-�
�tions.� In� some� cases� it� may� be� useful� to� logically� OR� the� BUSY� outputs�
�together� and� use� any� BUSY� indication� as� an� interrupt� source� to� flag� the�
�BUSY� (L)�
�MASTER� CE�
�Dual� Port�
�RAM�
�BUSY� (L)� BUSY� (R)�
�SLAVE� CE�
�Dual� Port�
�RAM�
�BUSY� (L)� BUSY� (R)�
�BUSY� (R)�
�4089� drw� 17�
�,�
�event� of� an� illegal� or� illogical� operation.� If� the� write� inhibit� function� of�
�BUSY� logic� is� not� desirable,� the� BUSY� logic� can� be� disabled� by� placing�
�the� part� in� slave� mode� with� the� M/� S� pin.� Once� in� slave� mode� the� BUSY�
�pin� operates� solely� as� a� write� inhibit� input� pin.� Normal� operation� can� be�
�programmed� by� tying� the� BUSY� pins� HIGH.� If� desired,� unintended�
�write� operations� can� be� prevented� to� a� port� by� tying� the� BUSY� pin� for�
�that� port� LOW.�
�The� BUSY� outputs� on� the� IDT7034� RAM� in� master� mode,� are� push-�
�pull� type� outputs� and� do� not� require� pull� up� resistors� to� operate.� If� these�
�RAMs� are� being� expanded� in� depth,� then� the� BUSY� indication� for� the�
�resulting� array� requires� the� use� of� an� external� AND� gate.�
�WIDTH� EXPANSION� WITH� BUSY� LOGIC�
�MASTER/SLAVE� ARRAYS�
�When� expanding� an� IDT7034� RAM� array� in� width� while� using�
�BUSY� logic,� one� master� part� is� used� to� decide� which� side� of� the� RAM�
�array� will� receive� a� BUSY� indication,� and� to� output� that� indication.� Any�
�number� of� slaves� to� be� addressed� in� the� same� address� range� as� the�
�master,� use� the� BUSY� signal� as� a� write� inhibit� signal.� Thus� on� the�
�IDT7034� RAM� the� BUSY� pin� is� an� output� if� the� part� is� used� as� a� master�
�(M/� S� pin� =� V� IH� ),� and� the� BUSY� pin� is� an� input� if� the� part� used� as� a� slave�
�(M/� S� pin� =� V� IL� )� as� shown� in� Figure� 3.�
�If� two� or� more� master� parts� were� used� when� expanding� in� width,� a�
�split� decision� could� result� with� one� master� indicating� BUSY� on� one� side�
�of� the� array� and� another� master� indicating� BUSY� on� one� other� side� of�
�the� array.� This� would� inhibit� the� write� operations� from� one� port� for� part�
�of� a� word� and� inhibit� the� write� operations� from� the� other� port� for� the�
�other� part� of� the� word.�
�The� BUSY� arbitration,� on� a� master,� is� based� on� the� chip� enable� and�
�address� signals� only.� It� ignores� whether� an� access� is� a� read� or� write.�
�In� a� master/slave� array,� both� address� and� chip� enable� must� be� valid�
�long� enough� for� a� BUSY� flag� to� be� output� from� the� master� before� the�
�actual� write� pulse� can� be� initiated� with� either� the� R/� W� signal� or� the� byte�
�enables.� Failure� to� observe� this� timing� can� result� in� a� glitched� internal�
�write� inhibit� signal� and� corrupted� data� in� the� slave.�
�SEMAPHORES�
�The� IDT7034� is� an� extremely� fast� Dual-Port� 4K� x� 18� CMOS� Static�
�RAM� with� an� additional� 8� address� locations� dedicated� to� binary�
�semaphore� flags.� These� flags� allow� either� processor� on� the� left� or� right�
�side� of� the� Dual-Port� RAM� to� claim� a� privilege� over� the� other� processor�
�for� functions� defined� by� the� system� designer’s� software.� As� an� ex-�
�ample,� the� semaphore� can� be� used� by� one� processor� to� inhibit� the�
�Figure� 3.� Busy� and� chip� enable� routing� for� both� width� and�
�depth� expansion� with� IDT7034� RAMs.�
�other� from� accessing� a� portion� of� the� Dual-Port� RAM� or� any� other�
�shared� resource.�
�The� Dual-Port� RAM� features� a� fast� access� time,� and� both� ports� are�
�completely� independent� of� each� other.� This� means� that� the� activity� on�
�the� left� port� in� no� way� slows� the� access� time� of� the� right� port.� Both� ports�
�are� identical� in� function� to� standard� CMOS� Static� RAM� and� can� be� read�
�from,� or� written� to,� at� the� same� time� with� the� only� possible� conflict�
�arising� from� the� simultaneous� writing� of,� or� a� simultaneous� READ/�
�WRITE� of,� a� non-semaphore� location.� Semaphores� are� protected�
�against� such� ambiguous� situations� and� may� be� used� by� the� system�
�program� to� avoid� any� conflicts� in� the� non-semaphore� portion� of� the�
�Dual-Port� RAM.� These� devices� have� an� automatic� power-down� fea-�
�ture� controlled� by� CE� ,� the� Dual-Port� RAM� enable,� and� SEM� ,� the�
�semaphore� enable.� The� CE� and� SEM� pins� control� on-chip� power� down�
�circuitry� that� permits� the� respective� port� to� go� into� standby� mode� when�
�not� selected.� This� is� the� condition� which� is� shown� in� Truth� Table� I� where�
�CE� and� SEM� are� both� HIGH.�
�Systems� which� can� best� use� the� IDT7034� contain� multiple� proces-�
�sors� or� controllers� and� are� typically� very� high-speed� systems� which� are�
�software� controlled� or� software� intensive.� These� systems� can� benefit�
�from� a� performance� increase� offered� by� the� IDT7034's� hardware�
�semaphores,� which� provide� a� lockout� mechanism� without� requiring�
�complex� programming.�
�Software� handshaking� between� processors� offers� the� maximum� in�
�system� flexibility� by� permitting� shared� resources� to� be� allocated� in�
�varying� configurations.� The� IDT7034� does� not� use� its� semaphore� flags�
�to� control� any� resources� through� hardware,� thus� allowing� the� system�
�designer� total� flexibility� in� system� architecture.�
�An� advantage� of� using� semaphores� rather� than� the� more� common�
�methods� of� hardware� arbitration� is� that� wait� states� are� never� incurred�
�in� either� processor.� This� can� prove� to� be� a� major� advantage� in� very�
�high-speed� systems.�
�HOW� THE� SEMAPHORE� FLAGS� WORK�
�The� semaphore� logic� is� a� set� of� eight� latches� which� are� indepen-�
�dent� of� the� Dual-Port� RAM.� These� latches� can� be� used� to� pass� a� flag,�
�or� token,� from� one� port� to� the� other� to� indicate� that� a� shared� resource�
�is� in� use.� The� semaphores� provide� a� hardware� assist� for� a� use�
�assignment� method� called� “Token� Passing� Allocation.”� In� this� method,�
�16�
�相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| IDT7035L20PFI | IC SRAM 144KBIT 20NS 100TQFP |
| IDT7037L20PFI | IC SRAM 576KBIT 20NS 100TQFP |
| IDT7038L15PFG | IC SRAM 1024KBIT 15NS 120TQFP |
| IDT7052L20G | IC SRAM 16KBIT 20NS 108PGA |
| IDT7054L20G | IC SRAM 32KBIT 20NS 108PGA |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| IDT7034L20PFI8 | 功能描述:IC SRAM 72KBIT 20NS 100TQFP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 存储器 系列:- 标准包装:72 系列:- 格式 - 存储器:RAM 存储器类型:SRAM - 同步 存储容量:9M(256K x 36) 速度:75ns 接口:并联 电源电压:3.135 V ~ 3.465 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 封装/外壳:100-LQFP 供应商设备封装:100-TQFP(14x14) 包装:托盘 其它名称:71V67703S75PFGI |
| IDT7034S15PF | 功能描述:IC SRAM 72KBIT 15NS 100TQFP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 存储器 系列:- 标准包装:45 系列:- 格式 - 存储器:RAM 存储器类型:SRAM - 双端口,异步 存储容量:128K(8K x 16) 速度:15ns 接口:并联 电源电压:3 V ~ 3.6 V 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 封装/外壳:100-LQFP 供应商设备封装:100-TQFP(14x14) 包装:托盘 其它名称:70V25S15PF |
| IDT7034S15PF8 | 功能描述:IC SRAM 72KBIT 15NS 100TQFP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 存储器 系列:- 标准包装:72 系列:- 格式 - 存储器:RAM 存储器类型:SRAM - 同步 存储容量:9M(256K x 36) 速度:75ns 接口:并联 电源电压:3.135 V ~ 3.465 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 封装/外壳:100-LQFP 供应商设备封装:100-TQFP(14x14) 包装:托盘 其它名称:71V67703S75PFGI |
| IDT7034S20PF | 功能描述:IC SRAM 72KBIT 20NS 100TQFP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 存储器 系列:- 标准包装:45 系列:- 格式 - 存储器:RAM 存储器类型:SRAM - 双端口,异步 存储容量:128K(8K x 16) 速度:15ns 接口:并联 电源电压:3 V ~ 3.6 V 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 封装/外壳:100-LQFP 供应商设备封装:100-TQFP(14x14) 包装:托盘 其它名称:70V25S15PF |
| IDT7034S20PF8 | 功能描述:IC SRAM 72KBIT 20NS 100TQFP RoHS:否 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 存储器 系列:- 标准包装:72 系列:- 格式 - 存储器:RAM 存储器类型:SRAM - 同步 存储容量:9M(256K x 36) 速度:75ns 接口:并联 电源电压:3.135 V ~ 3.465 V 工作温度:-40°C ~ 85°C 封装/外壳:100-LQFP 供应商设备封装:100-TQFP(14x14) 包装:托盘 其它名称:71V67703S75PFGI |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。