参数资料
| 型号: | ADV3200ASWZ |
| 厂商: | Analog Devices Inc |
| 文件页数: | 26/36页 |
| 文件大小: | 0K |
| 描述: | IC CROSSPOINT SWIT 32X32 176LQFP |
| 标准包装: | 1 |
| 功能: | 交叉点开关 |
| 电路: | 1 x 32:32 |
| 电压电源: | 单/双电源 |
| 电压 - 电源,单路/双路(±): | 5V,±2.5V,±3.3V |
| 电流 - 电源: | 250mA |
| 工作温度: | -40°C ~ 85°C |
| 安装类型: | 表面贴装 |
| 封装/外壳: | 176-LQFP |
| 供应商设备封装: | 176-LQFP-EP(24x24) |
| 包装: | 托盘 |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页当前第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页
ADV3200/ADV3201
Rev. 0 | Page 32 of 3
6
QNPN
QPNP
VNEG
VPOS
VOUTPUT
IOUTPUT
IOUTPUT, QUIESCENT
07
17
6-
1
11
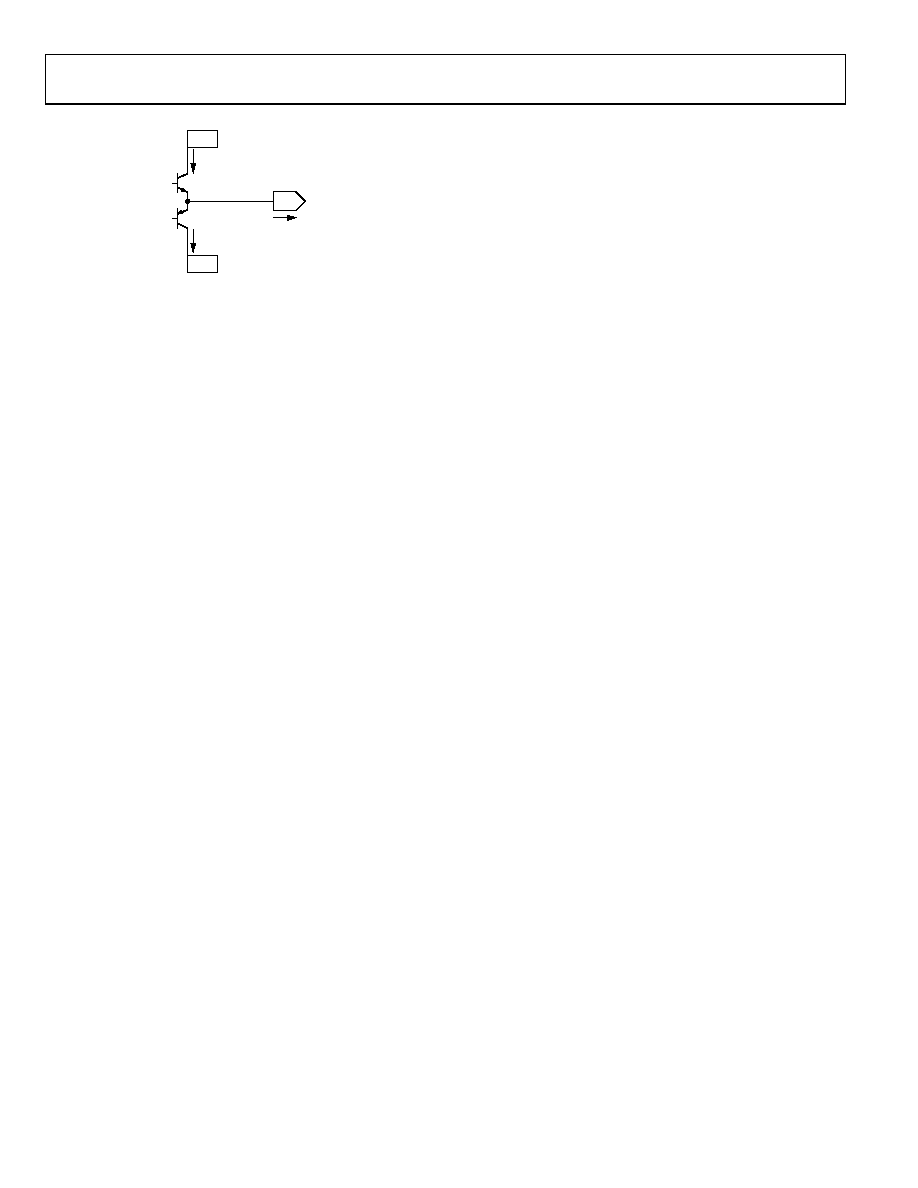
Figure 105. Simplified Output Stage
Example
For the ADV3200, in an ambient temperature of 85°C, with all
32 outputs driving 1 V rms into 150 Ω loads and power supplies
at ±2.5 V, follow these steps:
1.
Calculate the power dissipation of the ADV3200 using data
sheet quiescent currents. Disregard VDD current, which is
insignificant.
PD,QUIESCENT = (VPOS × IVPOS) + (VNEG × IVNEG)
PD,QUIESCENT = (2.5 V × 250 mA) + (2.5 V × 250 mA) = 1.25 W
2.
Calculate the power dissipation from the loads.
PD,OUTPUT = (VPOS – VOUTPUT,RMS) × IOUTPUT,RMS
PD,OUTPUT = (2.5 V – 1 V) × (1 V/150 Ω) = 10 mW
There are 32 outputs, therefore, 32 output currents.
nPD,OUTPUT = 32 × 10 mW = 0.32 W
3.
Subtract the quiescent output stage current for the number
of loads (32 in this example). The output stage is either
standing or driving a load, but the current needs to be
counted only once (valid for output voltages > 0.5 V).
PDQ,OUTPUT = (VPOS – VNEG) × IOUTPUT,QUIESCENT
PDQ,OUTPUT = (2.5 V – (–2.5 V)) × (0.95 mA) = 4.75 mW
There are 32 outputs, therefore, 32 output currents.
nPDQ,OUTPUT = 32 × 4.75 mW = 0.15 W
4.
Verify that the power dissipation does not exceed the
maximum allowed value.
PD,ON-CHIP = PD,QUIESCENT + nPD,OUTPUT nPDQ,OUTPUT
PD,ON-CHIP = 1.25 W + 0.32 W 0.15 W= 1.42 W
As shown in Figure 104 or Equation 1, this power dissipation is
below the maximum allowed dissipation for all ambient temper-
atures up to and including 85°C.
CROSSTALK
Many systems, such as broadcast video and KVM switches, that
handle numerous analog signal channels have strict require-
ments for keeping the various signals from influencing any of
the others in the system. Crosstalk is the term used to describe
the coupling of the signals of other nearby channels to a given
channel.
When there are many signals in close proximity in a system, as
is undoubtedly the case in a system that uses the ADV3200/
ADV3201, the crosstalk issues can be quite complex. A good
understanding of the nature of crosstalk and some definition of
terms is required in order to specify a system that uses one or
more crosspoint devices.
Types of Crosstalk
Crosstalk can be propagated by any of three means: electric
field, magnetic field, and sharing of common impedances. This
section explains these effects.
Every conductor can be both a radiator of electric fields and a
receiver of electric fields. The electric field crosstalk mechanism
occurs when the electric field created by the transmitter
propagates across a stray capacitance (for example, free space),
couples with the receiver, and induces a voltage. This voltage is
an unwanted crosstalk signal in any channel that receives it.
Currents flowing in conductors create magnetic fields that
circulate around the currents. These magnetic fields then
generate voltages in any other conductors whose paths they
link. The undesired induced voltages in these other channels are
crosstalk signals. The channels with crosstalk can be said to
have a mutual inductance that couples signals from one channel
to another.
The power supplies, grounds, and other signal return paths
of a multichannel system are generally shared by the various
channels. When a current from one channel flows in one of
these paths, a voltage that is developed across the impedance
becomes an input crosstalk signal for other channels that share
the common impedance.
All these sources of crosstalk are vector quantities, so the mag-
nitudes cannot simply be added together to obtain the total
crosstalk. In fact, there are conditions where driving additional
circuits in parallel in a given configuration can actually reduce
the crosstalk.
Areas of Crosstalk
A practical ADV3200/ADV3201 circuit must be mounted to
some sort of circuit board in order to connect it to power
supplies and measurement equipment. Great care has been
taken to create an evaluation board that adds minimum cross-
talk to the intrinsic device. This, however, raises the issue that
the crosstalk of a system is the combination of the intrinsic
crosstalk of the devices and the crosstalk of the circuit board to
which the devices are mounted. It is important to separate these
two areas when attempting to minimize the effect of crosstalk.
In addition, crosstalk can occur among the inputs to a cross-
point switch and among the outputs. It can also occur from
input to output. Techniques are discussed in the following
sections for diagnosing which part of a system is contributing
to crosstalk.
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ADV3203ASWZ | IC CROSSPOINT SWIT 32X16 176LQFP |
| ADV3205JSTZ | IC CROSSPOINT SWIT 16X16 100LQFP |
| ADV3220ACPZ-R7 | IC MULTIPLEXER 2:1 16LFCSP |
| ADV3222ARZ-R7 | IC MULTIPLEXER 4:1 16SOIC |
| ADV3225ACPZ | IC CROSSPOINT SW 16X8 72LFCSP |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| ADV3200-EVALZ | 功能描述:ADV3200 - Interface, Crosspoint Switch/Multiplexer Evaluation Board 制造商:analog devices inc. 系列:- 零件状态:有效 主要用途:接口,交叉点开关/多路复用器 嵌入式:- 使用的 IC/零件:ADV3200 主要属性:32 x 32 视频交叉点开关 辅助属性:图形用户界面 所含物品:板,线缆 标准包装:1 |
| ADV3201 | 制造商:AD 制造商全称:Analog Devices 功能描述:300 MHz, 32 × 32 Buffered Analog Crosspoint Switch |
| ADV3201ASWZ | 功能描述:IC CROSSPOINT SWIT 32X32 176LQFP RoHS:是 类别:集成电路 (IC) >> 接口 - 模拟开关,多路复用器,多路分解器 系列:- 应用说明:Ultrasound Imaging Systems Application Note 产品培训模块:Lead (SnPb) Finish for COTS Obsolescence Mitigation Program 标准包装:250 系列:- 功能:开关 电路:单刀单掷 导通状态电阻:48 欧姆 电压电源:单电源 电压 - 电源,单路/双路(±):2.7 V ~ 5.5 V 电流 - 电源:5µA 工作温度:0°C ~ 70°C 安装类型:表面贴装 封装/外壳:48-LQFP 供应商设备封装:48-LQFP(7x7) 包装:托盘 |
| ADV3201-EVALZ | 功能描述:ADV3201 - Interface, Crosspoint Switch/Multiplexer Evaluation Board 制造商:analog devices inc. 系列:- 零件状态:有效 主要用途:接口,交叉点开关/多路复用器 嵌入式:- 使用的 IC/零件:ADV3201 主要属性:32 x 32 视频交叉点开关 辅助属性:图形用户界面 所含物品:板,线缆 标准包装:1 |
| ADV3202 | 制造商:AD 制造商全称:Analog Devices 功能描述:300 MHz, 32 × 16 Buffered Analog Crosspoint Switch |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。