- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录80565 > M68LC302CPU20VCT (FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC) 4 CHANNEL(S), 10M bps, LOCAL AREA NETWORK CONTROLLER, PQFP100 PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | M68LC302CPU20VCT |
| 厂商: | FREESCALE SEMICONDUCTOR INC |
| 元件分类: | 微控制器/微处理器 |
| 英文描述: | 4 CHANNEL(S), 10M bps, LOCAL AREA NETWORK CONTROLLER, PQFP100 |
| 封装: | 14 X 14 MM, 1.40 MM HEIGHT, 0.50 MM PITCH, PLASITC, LQFP-100 |
| 文件页数: | 69/128页 |
| 文件大小: | 641K |
| 代理商: | M68LC302CPU20VCT |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页当前第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页第90页第91页第92页第93页第94页第95页第96页第97页第98页第99页第100页第101页第102页第103页第104页第105页第106页第107页第108页第109页第110页第111页第112页第113页第114页第115页第116页第117页第118页第119页第120页第121页第122页第123页第124页第125页第126页第127页第128页
ETHERNET Controller
4-6
MC68EN302 REFERENCE MANUAL
MOTOROLA
4.1.4 INTERRUPT VECTOR REGISTER (IVEC)
The IVEC register controls the interrupt vector generated by the Ethernet controller during
an interrupt acknowledge cycle. This register can only be written when the ETHER_EN bit
in the ECNTRL register is cleared. This register is reset to $000F.
15–8—Reserved.
Should be written to zero by the host processor. These bits are always read as zero.
VG—Vector Granularity.
0 = The interrupt vector is not modified to reflect the cause of the interrupt.
1 = The interrupt vector is modified to indicate the cause of the interrupt, replacing the
lower two bits of the interrupt vector according to the following table:
If multiple interrupt sources are present simultaneously and VG = 1, the INV bits will be set
based on the following priority (highest ot lowest);
1. Time critical interrupt.
2. Receive interrupt
3. Transmit interrupt
4. Non-time critical interrupt.
For example, if both RXB and TFINT interrupts are asserted, INV1–INV0 will equal 00.
Interrupt Vector1–0 represent the values of the two lower bits placed on the data bus during
an interrupt acknowledge cycle. VG is cleared by reset.
INV7–0—Interrupt Vector.
INV is the eight bit vector that the Ethernet controller places on the low byte of the data bus
during an interrupt acknowledge cycle.
4.1.5 INTERRUPT EVENT REGISTER (INTR_EVENT)
When an event occurs that sets a bit in the Interrupt Event Register, and the corresponding
bit in the interrupt mask register (INTR_MASK) is set, an interrupt will be generated. To clear
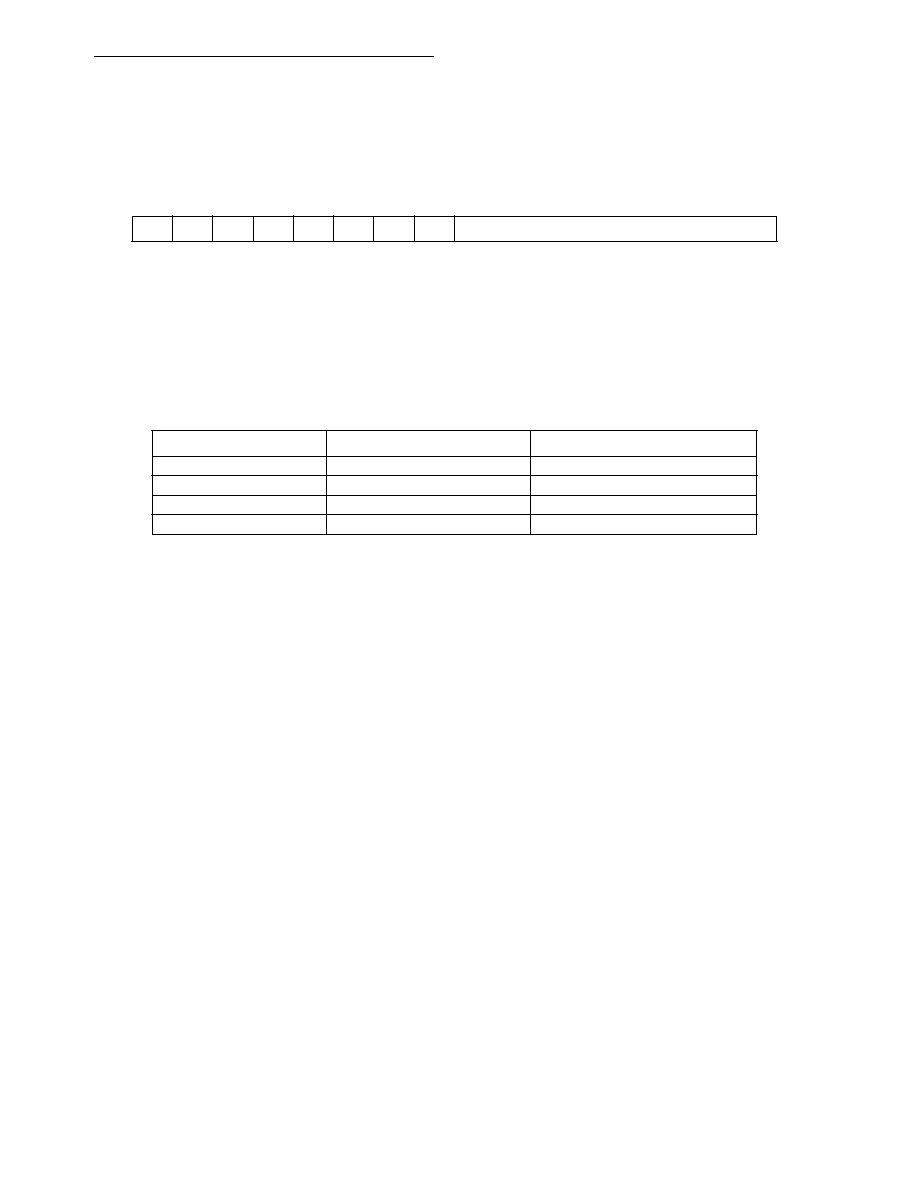
15
14
13
12
11
10
9876543210
00000000
INV<7:0>
INTERRUPT VECTOR1–0
CAUSE
EXAMPLES
00
Receive Interrupt
RFINT, RXB
01
Transmit Interrupt
TFINT, TXB
10
Non-Time Critical Interrupt
HBERR, BABR, BABT, GRA, BOD, EBERR
11
Time Critical Interrupt
BSY
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MC68030FE25C | 32-BIT, 25 MHz, MICROPROCESSOR, CQFP132 |
| MC68302CPV16VC | 4 CHANNEL(S), 10M bps, LOCAL AREA NETWORK CONTROLLER, PQFP144 |
| MC68331CFC16B1 | 32-BIT, 16 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP132 |
| MC68882CRC16A | 32-BIT, MATH COPROCESSOR, CPGA68 |
| MC68HC11E1VFN3 | 8-BIT, 3 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQCC52 |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| M68LGL061X | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:SUB ONLY CRT |
| M68LGL061XA | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:CRT OR M68LGL061X |
| M68LNK161X | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:CRT |
| M68LUQ085X | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:CRT |
| M68LZP195X | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:CRT |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。