- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录378056 > PM73487-PI (PMC-SIERRA INC) 622 Mbps ATM Traffic Management Device PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | PM73487-PI |
| 厂商: | PMC-SIERRA INC |
| 元件分类: | 数字传输电路 |
| 英文描述: | 622 Mbps ATM Traffic Management Device |
| 中文描述: | ATM/SONET/SDH SUPPORT CIRCUIT, PBGA503 |
| 封装: | EPBGA-503 |
| 文件页数: | 50/251页 |
| 文件大小: | 3126K |
| 代理商: | PM73487-PI |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页当前第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页第90页第91页第92页第93页第94页第95页第96页第97页第98页第99页第100页第101页第102页第103页第104页第105页第106页第107页第108页第109页第110页第111页第112页第113页第114页第115页第116页第117页第118页第119页第120页第121页第122页第123页第124页第125页第126页第127页第128页第129页第130页第131页第132页第133页第134页第135页第136页第137页第138页第139页第140页第141页第142页第143页第144页第145页第146页第147页第148页第149页第150页第151页第152页第153页第154页第155页第156页第157页第158页第159页第160页第161页第162页第163页第164页第165页第166页第167页第168页第169页第170页第171页第172页第173页第174页第175页第176页第177页第178页第179页第180页第181页第182页第183页第184页第185页第186页第187页第188页第189页第190页第191页第192页第193页第194页第195页第196页第197页第198页第199页第200页第201页第202页第203页第204页第205页第206页第207页第208页第209页第210页第211页第212页第213页第214页第215页第216页第217页第218页第219页第220页第221页第222页第223页第224页第225页第226页第227页第228页第229页第230页第231页第232页第233页第234页第235页第236页第237页第238页第239页第240页第241页第242页第243页第244页第245页第246页第247页第248页第249页第250页第251页
PM73487 QRT
PMC-Sierra, Inc.
PMC-980618
Issue 3
622 Mbps ATMTraffic Management Device
Released
Datasheet
38
lar to the SC1 and SC2 classes (Q
2
, Q
10
, Q
3
, Q
41
, Q
11
, ..., Q
7
, Q
15
, Q
2
, ...).
The transmit queue controller scheduler provides the following benefits:
QoS - the strict priority scheme among SC1, SC2, and GP SCs, and the weighted round-
robin algorithms allows satisfaction of QoS guarantees.
CDV minimization - the treatment of the strict priority SCs ensure that cells within these
SCs get timely service.
MCR guarantee - the timeslot table ensures all SCs will receive a minimum amount of
servicing (clearly, the aggregate bandwidth given to the SC1 and SC2 VCs affects the
remaining bandwidth to be divided between the GP SCs).
Fairness maximization - the weights of the SCs (1, 4, 16, or 64) allow different SCs to
support different bandwidth requirements (for example, high bandwidth SCs are assigned
64 and are serviced 64 times as often as low bandwidth SCs, which are assigned 1).
Output isolation - the cells of channels destined for different VOs are kept in separate data
structures. This helps isolate the effects of congestion on one VO from causing congestion
on another VO.
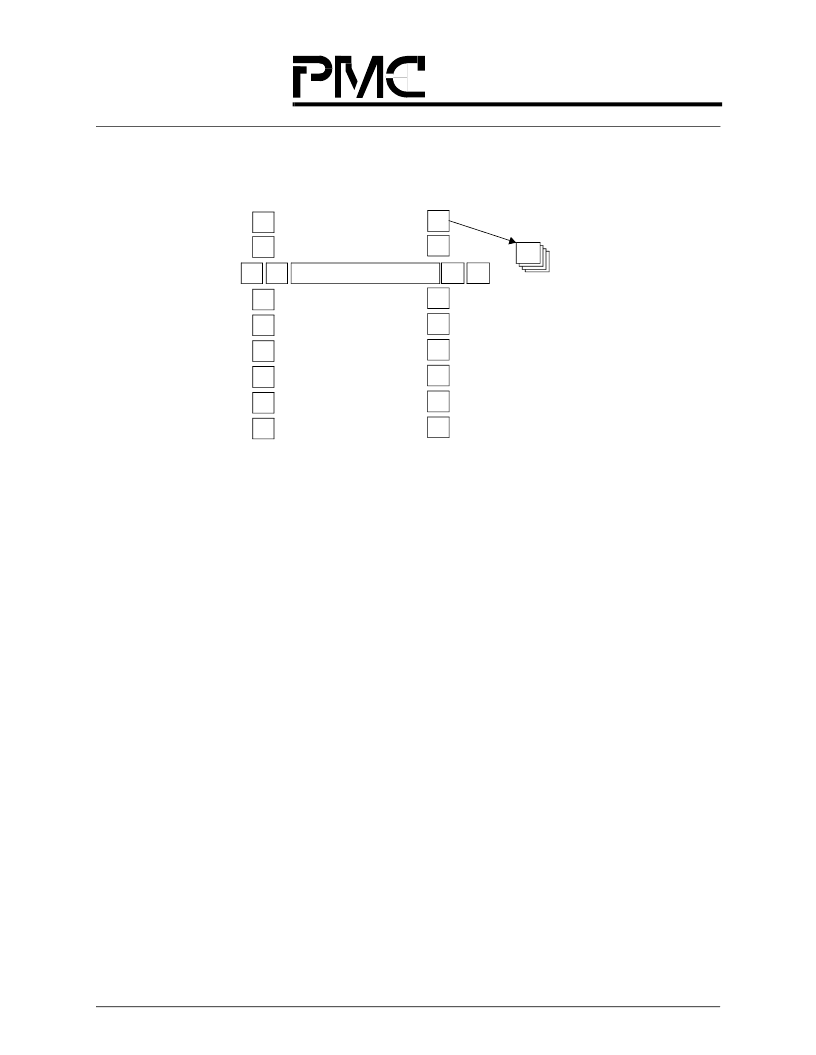
Figure 42. Transmit Service Class (SC) Map (Per VO)
Unicast Traffic
Multicast Traffic
Strict Priority SC1
Strict Priority SC2
Timeslot-Based Priority
General Purpose
Weighted Round-
Robin SCs
Q
0
Q
1
Q
2
S
0
S
1
Q
3
Q
4
Q
5
Q
6
Q
7
S
125
S
126
VC
Cells are FIFO-Queued
within an SC
Q
8
Q
9
Q
10
Q
11
Q
12
Q
13
Q
14
Q
15
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| PM73487 | 622 Mbps ATM Traffic Management Device |
| PM73488-PI | 5 Gbit/s ATM Switch Fabric Element |
| PM73488 | 5 Gbit/s ATM Switch Fabric Element |
| PM7349 | Ultraframer DS3/E3/DS2/E2/DS1/E1/DS0 |
| PM7350 | Dual Serial Link, PHY Multiplexer |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| PM73488 | 制造商:PMC 制造商全称:PMC 功能描述:5 Gbit/s ATM Switch Fabric Element |
| PM73488PI | 制造商:未知厂家 制造商全称:未知厂家 功能描述:Telecommunication IC |
| PM73488-PI | 制造商:Rochester Electronics LLC 功能描述: 制造商:PMC-Sierra 功能描述: |
| PM7349 | 制造商:PMC 制造商全称:PMC 功能描述:Quad J2, E3 and DS-3 Framer |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。