- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录98145 > ST7267R8T1L/XXX (STMICROELECTRONICS) 16-BIT, MROM, 30 MHz, RISC MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | ST7267R8T1L/XXX |
| 厂商: | STMICROELECTRONICS |
| 元件分类: | 微控制器/微处理器 |
| 英文描述: | 16-BIT, MROM, 30 MHz, RISC MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP64 |
| 封装: | 10 X 10 MM, LEAD FREE, TQFP-64 |
| 文件页数: | 120/189页 |
| 文件大小: | 1643K |
| 代理商: | ST7267R8T1L/XXX |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页第90页第91页第92页第93页第94页第95页第96页第97页第98页第99页第100页第101页第102页第103页第104页第105页第106页第107页第108页第109页第110页第111页第112页第113页第114页第115页第116页第117页第118页第119页当前第120页第121页第122页第123页第124页第125页第126页第127页第128页第129页第130页第131页第132页第133页第134页第135页第136页第137页第138页第139页第140页第141页第142页第143页第144页第145页第146页第147页第148页第149页第150页第151页第152页第153页第154页第155页第156页第157页第158页第159页第160页第161页第162页第163页第164页第165页第166页第167页第168页第169页第170页第171页第172页第173页第174页第175页第176页第177页第178页第179页第180页第181页第182页第183页第184页第185页第186页第187页第188页第189页
ST7267C8 ST7267R8
36/189
ST7 INTERRUPTS (Cont’d)
Servicing Pending Interrupts
As several interrupts can be pending at the same
time, the interrupt to be taken into account is deter-
mined by the following two-step process:
– the highest software priority interrupt is serviced,
– if several interrupts have the same software pri-
ority then the interrupt with the highest hardware
priority is serviced first.
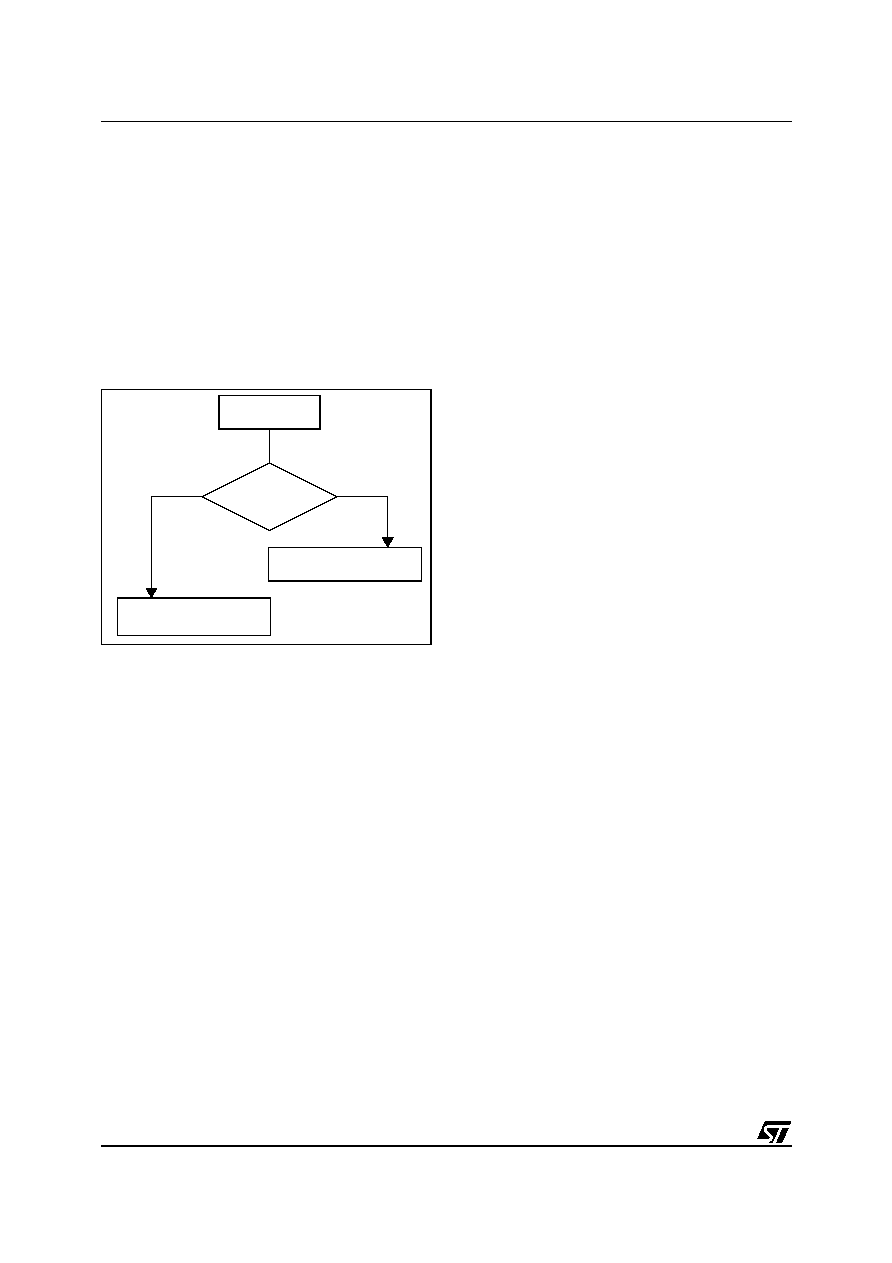
Figure 15 describes this decision process.
Figure 15. Priority Decision Process
When an interrupt request is not serviced immedi-
ately, it is latched and then processed when its
software priority combined with the hardware pri-
ority becomes the highest one.
Note 1: The hardware priority is exclusive while
the software one is not. This allows the previous
process to succeed with only one interrupt.
Note 2: RESET and TRAP are non maskable and
they can be considered as having the highest soft-
ware priority in the decision process.
Different Interrupt Vector Sources
Two interrupt source types are managed by the
ST7 interrupt controller: the non-maskable type
(RESET, TRAP) and the maskable type (external
or from internal peripherals).
Non-Maskable Sources
These sources are processed regardless of the
state of the I1 and I0 bits of the CC register (see
Figure 14). After stacking the PC, X, A and CC
registers (except for RESET), the corresponding
vector is loaded in the PC register and the I1 and
I0 bits of the CC are set to disable interrupts (level
3). These sources allow the processor to exit
HALT mode.
■ TRAP (Non Maskable Software Interrupt)
This software interrupt is serviced when the TRAP
instruction is executed. It will be serviced accord-
ing to the flowchart in Figure 14.
■ RESET
The RESET source has the highest priority in the
ST7. This means that the first current routine has
the highest software priority (level 3) and the high-
est hardware priority.
See the RESET chapter for more details.
Maskable Sources
Maskable interrupt vector sources can be serviced
if the corresponding interrupt is enabled and if its
own interrupt software priority (in ISPRx registers)
is higher than the one currently being serviced (I1
and I0 in CC register). If any of these two condi-
tions is false, the interrupt is latched and thus re-
mains pending.
■ External Interrupts
External interrupts allow the processor to exit from
HALT low power mode.
External interrupt sensitivity is software selectable
through the External Interrupt Control register
(EICR).
External interrupt triggered on edge will be latched
and the interrupt request automatically cleared
upon entering the interrupt service routine.
If several input pins of a group connected to the
same interrupt line are selected simultaneously,
these will be logically ORed.
■ Peripheral Interrupts
Usually the peripheral interrupts cause the MCU to
exit from HALT mode except those mentioned in
the “Interrupt Mapping” table.
A peripheral interrupt occurs when a specific flag
is set in the peripheral status registers and if the
corresponding enable bit is set in the peripheral
control register.
The general sequence for clearing an interrupt is
based on an access to the status register followed
by a read or write to an associated register.
Note: The clearing sequence resets the internal
latch. A pending interrupt (i.e. waiting for being
serviced) will therefore be lost if the clear se-
quence is executed.
PENDING
SOFTWARE
Different
INTERRUPTS
Same
HIGHEST HARDWARE
PRIORITY SERVICED
PRIORITY
HIGHEST SOFTWARE
PRIORITY SERVICED
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| ST7267C8T1/XXX | 16-BIT, MROM, 30 MHz, RISC MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP48 |
| ST72774S9T1/XXX | 8-BIT, MROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
| ST72E734J6D0 | 8-BIT, UVPROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, CDIP42 |
| ST72T774S9T1 | 8-BIT, OTPROM, 8 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PQFP44 |
| ST7294C6B6 | 8-BIT, MROM, 4 MHz, MICROCONTROLLER, PDIP28 |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| ST72681/R12 | 制造商:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:CONTROLLER FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE BUS-POWERED USB 2.0 FLASH DR - Trays |
| ST72681/S13 | 制造商:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:CONTROLLER FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE - Trays |
| ST7271 | 制造商:Panasonic Industrial Company 功能描述:IC |
| ST7271N5B1-CLF | 制造商:STMicroelectronics 功能描述: |
| ST727X4-EMU2B | 制造商:STMicroelectronics 功能描述:REALTIME EMULATOR BOARD - Bulk |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。