- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录199479 > TSB43AA82GGW (TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC) 2 CHANNEL(S), 400M bps, SERIAL COMM CONTROLLER, PBGA176 PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | TSB43AA82GGW |
| 厂商: | TEXAS INSTRUMENTS INC |
| 元件分类: | 微控制器/微处理器 |
| 英文描述: | 2 CHANNEL(S), 400M bps, SERIAL COMM CONTROLLER, PBGA176 |
| 封装: | PLASTIC, BGA-176 |
| 文件页数: | 113/146页 |
| 文件大小: | 770K |
| 代理商: | TSB43AA82GGW |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页第62页第63页第64页第65页第66页第67页第68页第69页第70页第71页第72页第73页第74页第75页第76页第77页第78页第79页第80页第81页第82页第83页第84页第85页第86页第87页第88页第89页第90页第91页第92页第93页第94页第95页第96页第97页第98页第99页第100页第101页第102页第103页第104页第105页第106页第107页第108页第109页第110页第111页第112页当前第113页第114页第115页第116页第117页第118页第119页第120页第121页第122页第123页第124页第125页第126页第127页第128页第129页第130页第131页第132页第133页第134页第135页第136页第137页第138页第139页第140页第141页第142页第143页第144页第145页第146页
43
4.2.3
Exception to the Rule
By intentionally controlling tLabel, the response of a request packet from the ATF can be received by the DRF. This
method can be used when the size of a response packet is larger than the size of the ARF. As shown below, a request
packet with tlabel 01_xxxx is transmitted from the ATF but received by the DRF.
PACKET INPUT THROUGH 70h to 78h
FIFOs
tLabel
tCode
Transmit FIFO
Receive FIFO
01_xxxx
Request packet
ATF
DRF
NOTE: Combinations other than that specified are not recommended.
4.3
Asynchronous Transmit FIFO (ATF)
Asynchronous transmit refers to the use of the ATF interface. It is configurable in register 2Ch (ATF satus register).
To transmit packets, the 1394 asynchronous headers and the data are loaded into the ATF interface by the host. The
host accesses the ATF FIFO through registers 70h78h with the appropriate tLabel and tCode described in
Section 4.2. The asynchronous header must fit the form described in Section 4.3.1.
4.3.1
Generic Quadlet and Block Transmit
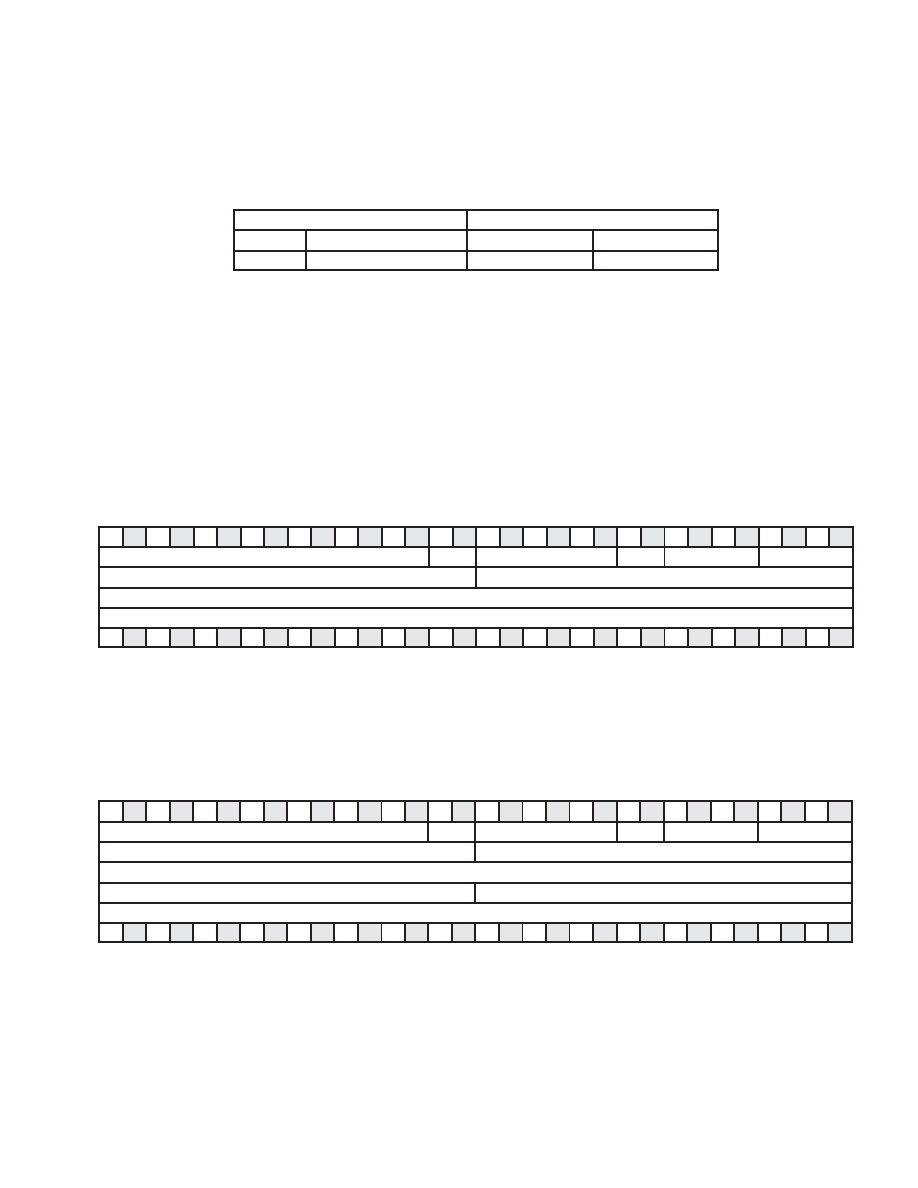
The quadlet-transmit format is shown in Figure 41. The first quadlet contains packet control information. The second
and third quadlets contain the 64-bit, quadlet-aligned address. The fourth quadlet is data used only for write requests
and read responses. For read requests and write responses, the quadlet data field is omitted.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Reserved
spd
tLabel
rt
tCode
prior
destination ID
destination_offset_high
destination_offset_low
quadlet data
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Figure 41. Generic Transmit Format of Packet With Quadlet Data
The block-transmit format is shown in Figure 42 and a description of each field is shown in Table 41. The first
quadlet contains packet-control information. The second quadlet contains the bus and node number of the destination
node, and the last 16 bits of the second quadlet and all of the third quadlet contain the 48-bit quadlet-aligned
destination offset address. The first 16 bits of the fourth quadlet contains the size of the data in the packet. The
remaining 16 bits of the fourth quadlet represent the extended_tCode field (see Table 6-10 of the IEEE 1394-1995
standard for more information on extended tCodes). The block data, if any, follows the extended_tCode.
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Reserved
spd
tLabel
rt
tCode
prior
destination ID
destination_offset_high
destination_offset_low
data_length
extended_tCode
block data
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Figure 42. Generic Transmit Format of Packet With Block Data
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| TSB43DA42GHCR | PCI BUS CONTROLLER, PBGA196 |
| TSB500SK02 | 30 A, BARRIER STRIP TERMINAL BLOCK, 1 ROW, 1 DECK |
| TSB500SK10MDS | 30 A, BARRIER STRIP TERMINAL BLOCK, 1 ROW, 1 DECK |
| TSB5000331DS | 30 A, BARRIER STRIP TERMINAL BLOCK, 1 ROW, 1 DECK |
| TSB5000831 | 30 A, BARRIER STRIP TERMINAL BLOCK, 1 ROW, 1 DECK |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|---|
| TSB43AA82GHH | 制造商:Texas Instruments 功能描述: |
| TSB43AA82I | 制造商:TI 制造商全称:Texas Instruments 功能描述:1394 INTEGRATED PHY AND LINK LAYER CONTROLLER |
| TSB43AA82IGGW | 功能描述:1394 接口集成电路 2Port Hi Perf Integ Phy&Link Layer Chip RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 类型:Link Layer Controller 工作电源电压: 封装 / 箱体:LQFP 封装:Tray |
| TSB43AA82PGE | 功能描述:1394 接口集成电路 2Port Hi Perf Integ Phy&Link Layer Chip RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 类型:Link Layer Controller 工作电源电压: 封装 / 箱体:LQFP 封装:Tray |
| TSB43AA82PGEG4 | 功能描述:1394 接口集成电路 2Port Hi Per Int Phy & Link Layer Chip RoHS:否 制造商:Texas Instruments 类型:Link Layer Controller 工作电源电压: 封装 / 箱体:LQFP 封装:Tray |
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。