- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > PDF目录385639 > MT48V4M32LFFC (Micron Technology, Inc.) SYNCHRONOUS DRAM PDF资料下载
参数资料
| 型号: | MT48V4M32LFFC |
| 厂商: | Micron Technology, Inc. |
| 英文描述: | SYNCHRONOUS DRAM |
| 中文描述: | 同步DRAM |
| 文件页数: | 21/61页 |
| 文件大小: | 1400K |
| 代理商: | MT48V4M32LFFC |
第1页第2页第3页第4页第5页第6页第7页第8页第9页第10页第11页第12页第13页第14页第15页第16页第17页第18页第19页第20页当前第21页第22页第23页第24页第25页第26页第27页第28页第29页第30页第31页第32页第33页第34页第35页第36页第37页第38页第39页第40页第41页第42页第43页第44页第45页第46页第47页第48页第49页第50页第51页第52页第53页第54页第55页第56页第57页第58页第59页第60页第61页
21
128Mb: x16, x32 Mobile SDRAM
MobileY95W_3V_F.p65 – Rev. F; Pub. 9/02
Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
128Mb: x16, x32
MOBILE SDRAM
ADVANCE
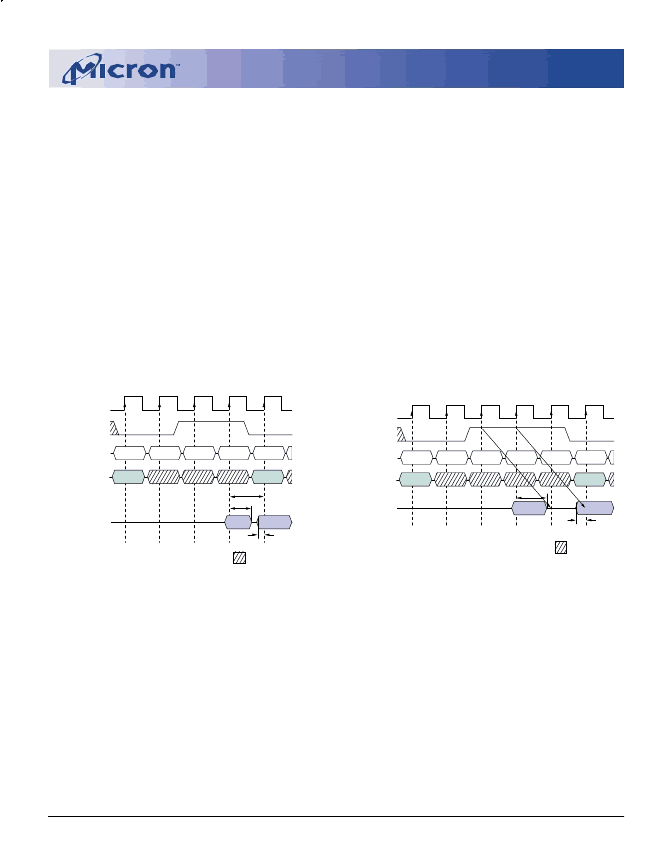
Data from any READ burst may be truncated with a
subsequent WRITE command, and data from a fixed-
length READ burst may be immediately followed by data
from a WRITE command (subject to bus turnaround
limitations). The WRITE burst may be initiated on the
clock edge immediately following the last (or last de-
sired) data element from the READ burst, provided that I/
O contention can be avoided. In a given system design,
there may be a possibility that the device driving the
input data will go Low-Z before the SDRAM DQs go High-
Z. In this case, at least a single-cycle delay should occur
between the last read data and the WRITE command.
The DQM input is used to avoid I/O contention, as
shown in Figures 9 and 10. The DQM signal must be
asserted (HIGH) at least two clocks prior to the WRITE
command (DQM latency is two clocks for output buffers)
DON’T CARE
READ
NOP
NOP
NOP
NOP
DQM
CLK
DQ
D
OUT
n
T2
T1
T4
T3
T0
COMMAND
ADDRESS
BANK,
COL
n
WRITE
D
IN
b
BANK,
COL
b
T5
DS
t
HZ
t
NOTE:
A CAS latency of three is used for illustration. The
READ command
may be to any bank, and the WRITE command may be to any bank.
Figure 10
READ to WRITE With
Extra Clock Cycle
Figure 9
READ to WRITE
DON’T CARE
READ
NOP
NOP
WRITE
NOP
CLK
T2
T1
T4
T3
T0
DQM
DQ
D
OUT
n
COMMAND
D
IN
b
ADDRESS
BANK,
COL
n
BANK,
COL
b
DS
t
HZ
t
t
CK
NOTE:
A CAS latency of three is used for illustration. The
READ
command may be to any bank, and the WRITE command
to suppress data-out from the READ. Once the WRITE
command is registered, the DQs will go High-Z (or re-
main High-Z), regardless of the state of the DQM signal,
provided the DQM was active on the clock just prior to
the WRITE command that truncated the READ com-
mand. If not, the second WRITE will be an invalid WRITE.
For example, if DQM was LOW during T4 in Figure 10,
then the WRITEs at T5 and T7 would be valid, while the
WRITE at T6 would be invalid.
The DQM signal must be de-asserted prior to the
WRITE command (DQM latency is zero clocks for input
buffers) to ensure that the written data is not masked.
Figure 9 shows the case where the clock frequency allows
for bus contention to be avoided without adding a NOP
cycle, and Figure 10 shows the case where the additional
NOP is needed.
相关PDF资料 |
PDF描述 |
|---|---|
| MT49H16M16 | THERMISTOR PTC 100OHM 110DEG RAD |
| MT49H16M16FM | REDUCED LATENCY DRAM RLDRAM |
| MT49H8M32 | THERMISTOR PTC 100OHM 120DEG RAD |
| MT49H8M32FM | REDUCED LATENCY DRAM RLDRAM |
| MT4C1M16E5DJ-6 | EDO DRAM |
相关代理商/技术参数 |
参数描述 |
|---|
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。